
The masks at the pilot stations will incorporate microphones to allow internal and external communications.

No matter which type of continuous flow system you use, you'll have the choice of a nasal cannula or a rebreather mask. A regulator is installed to reduce storage cylinder pressure to a usable level. Above 41,000', the regulations of most states require that one pilot wear an oxygen mask at all times, even when quick donning masks are fitted. The aerox Quick Comfort series diluter demand mask comes standard with an electret microphone and an inflatable Quick Comfort head harness. Depending upon the aircraft type, regulators can be constant flow or diluter-demand. Aerox 4110-712 Series Oxygen Mask FAA-TSO, MH E-Z Breathe II Boom Cannula Eds For Pulse Demand, Aerox High Duration Aviation Oxygen Systems. Quiz: 6 Questions To See How Much You Know About Approach Charts, How To Plan Your Arrival At An Unfamiliar Airport, When Can You Go Below MDA Or DA On An Instrument Approach? The higher the altitude, the lower theTime of Useful Consciousness: This article describes the systems onboard commercial transport aircraft designed to supply supplemental oxygen to crew and passengers when required to sustain life. Quiz: Can You Answer These 6 Instrument Checkride Questions? Item qualifies for free ground shipping. This system uses a face-tight seal to ensure cabin air doesn't unintentionally mix into the mask. You don't need to wear a mask while flying single-pilot under FAR Part 91 as long as the cabin altitude stays at or below 35,000 feet. After you inhale air into your lungs, atmospheric pressure forces oxygen through your lungs' membranes and into your bloodstream. Re-breather masks are limited to 25,000 feet. If you're flying something that can get higher, you'll probably have a "diluter demand" system. : Boldmethod Live, How To Find Cloud Top Heights For An IFR Flight: Boldmethod Live, Setting Up The Perfect VFR Arrival To An Airport: Boldmethod Live, 8 Tips For Keeping Your Logbooks Clean, Professional, And Interview-Ready, 6 Questions You Should Be Prepared To Answer During Your CFI Interview, Why Calling 'Go-Around' Is An Action, Not A Decision Point, How To Pick The Best Flight School For You, Fatigued Flight Crew Misses Two Altitude Restrictions On Departure. Would You Go?
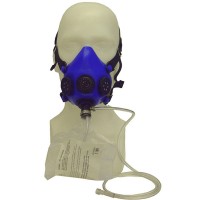
The total number of oxygen dispensing units shall exceed the number of passenger and cabin crew seats by at least 10 per cent.

For aircraft which routinely fly above 25,000', masks are generally of the "quick-donning" variety. In some cases, you'll actually dial an altitude into the regulator. In non-pressurised aircraft which routinely fly above 10,000', passenger oxygen is typically provided by either a fixed or a portable system. Pressurised aircraft which have a certified maximum altitude of 25,000' or less do not require passenger oxygen systems subject to the aircraft being able to descend to 13,000' or below within 4 minutes of loss of pressurisation. While we can't be sure it's a factor in either of the two accidents, hypoxia's a likely suspect. Airlines make a point during their safety presentation of pointing out that the bag may not inflate as, in the past, lack of bag inflation has lead some passengers to believe that their mask was not working and to remove it resulting in. Consult the appropriate documentation provided by the aircraftState of Registryfor specific criteria. But few learn about the different types of oxygen systems. As you climb, atmospheric pressure decreases, and the amount of oxygen forced into your blood also decreases. Oxygen for the use of the flight deck occupants is normally stored as pressurised gas in one or more tanks or cylinders.

Portable systems consist of a storage tank, a regulator and one or more passenger masks. Fax: 800-329-3020, West - Corona, CA
Quiz: Could You Handle These 6 Multi-Engine Failures? An operator shall ensure that passengers are made familiar with the location and use of: d) oxygen dispensing equipment, if the provision of oxygen for the use of passengers is prescribed An aeroplane intended to be operated at flight altitudes at which the atmospheric pressure is less than 700 hPa (see Note 1) in personnel compartments shall be equipped with oxygen storage and dispensing apparatus, A flight to be operated at flight altitudes at which the atmospheric pressure in personnel compartments will be less than 700 hPa shall not be commenced unless sufficient stored breathing oxygen is carried to supply: a) all crew members and 10 per cent of the passengers for any period in excess of 30 minutes that the pressure in compartments occupied by them will be between 700 hPa and 620 hPa; and b) the crew and passengers for any period that the atmospheric pressure in compartments occupied by them will be less than 620 hPa. The percentage of oxygen in the air doesn't change - it's still 21 percent. At altitudes lower than the designed optimum altitude, it will provide more oxygen than is actually required. There are three main types of oxygen systems to keep you safe - and all are meant for different altitudes. IFR Cross Country Into Low Ceilings And Scattered Storms, How To Circle-To-Land From An Instrument Approach, How To Time Your Flare For A Perfect Landing, How To Land With An Asymmetric Flap Failure, 7 Factors Every Pilot Should Consider Before Flying Around Thunderstorms, How To Fly An Approach To Landing Through Turbulence, Solo Endorsements: Understanding Basic Solo Requirements, Solo Endorsements: Understanding Solo Cross-Country Requirements, The Difference Between Decision Altitude (DA) and Decision Height (DH). source: Cabin Decompression and Hypoxia by Mark Wolff, PIA Air Safety Publication, 2006. Combine with 5110-100 Aerox Smoke Goggles and portable bottle for a standalone emergency kit! Since it automatically mixes oxygen and air only as you inhale, a diluter-demand system generally lasts longer than continuous flow. For pressurised aircraft which are certified to operate above 25,000', emergency oxygen equipment must be available. But, most systems are designed to keep you safe up to 25,000 feet. Copyright 2022 CFI Notebook, All rights reserved. Either way, the operation is simple. The most basic - and inexpensive - version pushes a standard rate of oxygen to each mask. Note 2:National or Regional Authoritiesuse the ICAO guidance as the basis for their regulations. Not a good idea. As you climb and decrease blood-oxygen, you'll eventually get hypoxic, pass out, and drone off unconscious until you run out of gas.

Quick Donning High-Altitude Diluter Demand Mask, Oxygen Filling Adapters and Filling Systems, Oxygen Bottles and Installed Oxygen Systems, 4110-155 Stowage Cup for Diluter Demand Mask, 5110-100 Aerox Smoke Goggles with tear shield. The bands are adjustable to accomodate passengers of different sizes. You can find portable continuous flow systems, and many light turbocharged aircraft have them built in. But, before you get into masks, you should understand what they're trying to do. This is exhausting - it takes a significant amount of force to exhale, you'll be tired after several hours on a pressure-demand system. Given that oxygen can be a hazardous chemical in the aviation environment, Preventative safety measures further include the wear of a, Additional considerations for other operations, including. What do you do if your equipment malfunctions? Other oxygen sources carried on pressurised commercial aircraft include supplemental oxygen tank and masks units for medical use and oxygen generator equipped smoke hoods for crew use in the event that it is necessary to fight an on board fire. An easy acronym to remember how is "PRICE: Before servicing any aircraft with oxygen, consult the specific aircraft service manual to determine the type of equipment required and procedures to be used, Observe precautions whenever servicing aircraft oxygen systems, Oxygen system servicing should be accomplished only when the aircraft is outside of the hangars, Personal cleanliness and good housekeeping are imperative when working with oxygen, Oxygen under pressure and petroleum products create spontaneous results when in contact with each other, Service people should be certain to wash dirt, oil, and grease (including lip salves and hair oil) from their hands and tools before working around oxygen equipment, Aircraft with permanently installed oxygen tanks usually require two persons to accomplish servicing of the system, One should remain at the service equipment control valves, with the others located where he or she can observe the aircraft system pressure gauges, Oxygen system servicing is not recommended during aircraft fueling operations or while other work is performed that could provide a source of ignition, Oxygen system servicing while passengers are on board the aircraft is not recommended, A pilot or passenger who intends to fly after scuba diving should allow the body sufficient time to rid itself of excess nitrogen absorbed during diving, Decompression sickness can occur from evolved gas creating a serious in-flight emergency, The recommended waiting time before going to flight altitudes of up to 8,000 feet is at least 12 hours after diving which has not required controlled ascent (non-decompression stop diving), and at least 24 hours after diving which has required controlled ascent (decompression stop diving), The waiting time before going to flight altitudes above 8,000 feet should be at least 24 hours after any SCUBA dive, These recommended altitudes are actual flight altitudes above mean sea level (AMSL) and not pressurized cabin altitudes, This takes into consideration the risk of decompression of the aircraft during flight, Note that while the percentage of oxygen in the atmosphere does not decrease, pressure for the body to absorb it does, necessitating supplemental oxygen, Note the connection between supplemental oxygen and, These rules are in place because others have died from it, At night, especially when tired, these effects may occur as low as 5,000 feet, Therefore, for optimum protection, pilots are encouraged to use supplemental oxygen above 10,000 feet cabin altitude during the day and above 5,000 feet at night, While subjective, oxygen use when operating near the required altitudes for it may also improve alertness and therefore decision making, Realize that while operating near, but below, altitudes requiring oxygen, passengers may still find themselves experiencing distress without it. Quiz: Do You Know These 6 Light Gun Signals? Please note, Aircraft Spruce's personnel are not certified aircraft mechanics and can only provide general support and ideas, which should not be relied upon or implemented in lieu of consulting an A&P or other qualified technician. | Privacy Policy | Terms of Service | Sitemap | Patreon | Contact, Private pilot supplemental oxygen system airman certification standards, Aeronautical Information Manual (8-1-2) Effects of Altitude, Federal Aviation Administration - Oxygen Equipment Use in General Aviation Operations, Federal Aviation Administration - Pilot/Controller Glossary, Federal Aviation Regulations (91.211) Supplemental Oxygen, Flying and Diving - A Unique Health Concern, Pilot Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge (6-34) Oxygen Systems, Supplemental oxygen provides pilot's operating at high altitudes to counteract the effect of decreasing pressure, particularly hypoxia, Operations at higher altitudes will drive the, Aircraft designed to operate at higher altitudes will normally have an oxygen generation system, Aircraft designed to operate at low altitudes will normally have a portable oxygen system. Select the mask size, hose length, and oxygen connection below. An aeroplane intended to be operated at flight altitudes at which the atmospheric pressure is less than 376 hPa or which, if operated at flight altitudes at which the atmospheric pressure is more than 376 hPa , cannot descend safely within four minutes to a flight altitude at which the atmospheric pressure is equal to 620 hPa shall be provided with automatically deployable oxygen equipment. The emergency oxygen supply must last a minimum of 10 minutes. But, at 18,000 feet, the atmospheric pressure is half that of sea-level. The altitude compensating continuous-flow system automatically adjusts the oxygen flow rate as you climb or descend.

When you think of an oxygen mask, you probably either think of the thing hanging around a fighter pilot's neck, or one of those little yellow dixie cups that drop from the overhead panels of an airliner. Let's take a look.

At low altitudes, it pushes too much oxygen. As an example, at 8000', the regulator might send 100% ambient air to the mask whereas at 41000', it would provide 100% oxygen. For diluter-demand systems, selectors for normal, 100% and positive pressure maybe incorporated into the mask itself. If the aircraft is not capable of achieving the descent profile or the route structure does not allow the descent due to terrain, an oxygen system must be fitted in the aircraft as per the provisions which apply to aircraft which are certified to fly at higher altitudes (above 25,000'). Supply Press Range: 55 to 70 Psi * (0.37 to 0.48 Mpa), Operating Temp Range: +20 0 to +1200 F ** (-290 to +490C). When installed, diluter-demand regulators will be located at each crew position. 2021 All Rights Reserved. Please note other excluded items on the same order may incur a freight charge.

And, how can you tell if you're hypoxic?

For new airline pilots and those upgrading to advanced aircraft, VNAV is one of the biggest automation hurdles to understand. Overhaul: Aerox recommends every 3 years. The mask could be of the "full face" variety incorporating smoke goggles or a "mouth and nose" type mask with smoke goggles available separately. Some aircraft utilize cylinders of pressurised oxygen to meet this requirement but most types are fitted with.

If a LOX system is installed, a LOX converter, which facilitates the transformation of the oxygen from a liquid to a gaseous state, will also be installed. Quiz: Do You Know These 5 Common IFR Phrases? There are a variety of different oxygen systems and delivery methods available to general and commercial aviation, including: Generally used on large aircraft in case of an emergency to provide a 10 minute supply of oxygen, Activated by a lanyard on the oxygen mask, as the user pulls the mask to their face, a chemical reaction with sodium chlorate is triggered, Once this system is activated, it must burn out, requiring replacement, Chemical oxygen is lightweight and compact, No more than 0.005 ml of water per 1 liter of oxygen = 99.5% O, Portable gaseous oxygen system provides oxygen when required for aircraft which lack an integral oxygen system, These systems are used for passengers or crew members when the aircraft oxygen systems services only the pilot and copilot, or when the duties of the crew require them to move about the aircraft, A portable unit weighs approximately 20 pounds and typically consists of: lightweight steel oxygen cylinder (usually 1800 Pounds per Square Inch (PSI), capacity vary), associated plumbing, combined flow control/reducing valve pressure gauge, and a breathing mask and connecting hose, On-Board Oxygen Generating System, or OBOGS, converts engine compressor bleed air to oxygen-rich breathing air and pressurized air for at the correct pressure and temperature, OBOGS provides a continuous supply of breathing air for crew while the engine is operating, Components consist of a heat exchanger, concentrator, regulator, and associated plumbing, Liquid oxygen systems, or LOX, is used in some jet aircraft because LOX storage occupies less space and weigh less than those used for gaseous oxygen, LOX systems typically consists of converters, check valves and manifolds, oxygen heat exchanger, oxygen/vent airflow control panel, liquid quantity indicator, and a breathing mask with connecting hoses, There are numerous types and designs of oxygen masks in use, The most critical factor in oxygen mask use is to ensure the masks and oxygen system are compatible, Crew masks are fitted to the user's face with a minimum of leakage and usually contain a microphone, Most masks are the oronasal type, which covers only the mouth and nose, A passenger mask may be a simple, cup-shaped rubber molding sufficiently flexible to prevent individual fitting, It may have a simple elastic head strap, or the passenger may hold it to his or her face, All oxygen masks should be clean to reduce the danger of infection and prolong the life of the mask, To clean the mask, wash it with a mild soap and water solution and rinse it with clear water, If a containing a microphone, use a clean swab, instead of running water, to wipe off the soapy solution, A gauze pad that has been soaked in a water solution of Merthiolate can be used to swab out the mask, This solution used should contain a one-fifth teaspoon of Merthiolate per quart of water, Wipe the mask with a clean cloth and air dry, Both pressure and diluter-demand systems use a diaphragm operated demand valve, which opens when suction from inhalation is present, A cannula is an ergonomic piece of plastic tubing that runs under the nose and is often used to administer oxygen in non-pressurized aircraft [, Cannulas are typically more comfortable than masks and can be used up to 18,000', Many cannulas have a flow meter in the line, and if equipped, a periodic check of the green flow detector should be part of a pilot's regular scan, Passenger aircraft generally utilize continuous-flow oxygen systems, The passenger mask typically has a reservoir bag, which collects oxygen from the continuous-flow oxygen system when the mask user is exhaling, The oxygen collected in the reservoir bag allows a higher aspiratory flow rate during the inhalation cycle, which reduces the amount of air dilution, Ambient air is added to the supplied oxygen during inhalation after the reservoir bag oxygen supply is depleted, Portable electrical pulse-demand oxygen systems deliver oxygen by detecting an individual's inhalation effort and provide oxygen flow during the initial portion of inhalation, Pulse demand systems do not waste oxygen during the breathing cycle because oxygen only delivers during inhalation, Compared to continuous-flow systems, the pulse-demand method of oxygen delivery can reduce the amount of oxygen needed by 50-85%, Most pulse-demand oxygen systems also incorporate an internal barometer that automatically compensates for changes in altitude by increasing the amount of oxygen delivered for each pulse as altitude is increased [, These systems can be either built in or portable, Check valves allow for exhaled air to exit the mask at high altitudes completely, General flow rates are 120 liters per hour for crew and 90 liters per hour for passengers, Diluter-demand oxygen systems supply oxygen only when the user inhales through the mask, An auto-mix lever allows the regulators to automatically mix cabin air and oxygen or supply 100% oxygen, depending on the altitude, The demand mask provides a tight seal over the face to prevent dilution with outside air, A pilot who has a beard or mustache should ensure it will not interfere with the sealing of the oxygen mask, Pressure-demand oxygen systems are similar to diluter demand oxygen equipment, except that oxygen is supplied to the mask under pressure at cabin altitudes above 34,000', Pressure-demand regulators create airtight and oxygen-tight seals, but they also provide a positive pressure application of oxygen to the mask facepiece that allows the user's lungs to pressurize with oxygen, Pressure-demand is used above 40,000' because even with 100% O, Some systems may have a pressure-demand mask with the regulator attached directly to the mask rather than mounted on the instrument panel or other area within the flight deck, The mask-mounted regulator eliminates the problem of a long hose that must be purged of air before 100% oxygen begins flowing into the mask, Aircraft oxygen stores in high-pressure system containers of 1,800-2,200 PSI, When the ambient temperature surrounding an oxygen cylinder decreases, the pressure within that cylinder decreases because pressure varies directly with temperature if the volume of a gas remains constant, If indicated pressure on a supplemental oxygen cylinder drops, there is no reason to suspect depletion of the oxygen supply, which has compressed due to storage of the containers in an unheated area of the aircraft, High-pressure oxygen containers have markings with the psi tolerance (i.e., 1,800 psi) before filling the container to that pressure, Service containers with aviation oxygen only, which is 100% pure oxygen, Industrial oxygen is not intended for breathing and may contain impurities, and facepiece oxygen masks may contain water vapor that can freeze in the regulator when exposed to cold temperatures, To assure safety, pilots should do periodic inspection and servicing of the oxygen system, Oxygen is an oxidizer, supporting combustion, and an extremely hazardous material in the aviation environment, Acting as a catalyst, small sparks or fires in the presence of combustibles such as oils, fuels, and other chemicals can quickly grow, Purge hoses before coupling to aircraft filler valves to avoid contamination, Containers need to be filled in a controlled manner to avoid overheating, Keep oil and grease away from oxygen equipment, including tools and protective clothing to avoid contamination, Use spark-free tools (brass) when servicing oxygen systems, Do not open valves of an oxygen system or cylinder when a flame, electrical arc, or any other source of ignition is in the immediate area, Take extreme caution not to touch implements containing liquid oxygen without gloves due to the extremely low temperature, Use protective clothing when working with LOX including gloves, coveralls, face shields, and LOX boots, Never seal or cap the vent port of a LOX system, Vent design ensures sufficient flow capacity to carry away LOX that may escape, The expansion ratio of liquid oxygen is 862 to 11-liquid oxygen at atmospheric pressure will a generate pressure of up to 12,000 PSI, If allowed to evaporate in a sealed container or system which has no relief provisions, LOX could cause an explosion, Never saturate cloth, wood, grease, oil paint, or tar with LOX, LOX by itself will not burn, but mixing it with any material will cause the LOX to boil and splash violently with possible combustion, A pulse oximeter is a device that measures the amount of oxygen in an individual's blood, in addition to heart rate, This non-invasive device measures the color changes that red blood cells undergo when they become saturated with oxygen, By transmitting a special light beam through a fingertip to evaluate the color of the red cells, a pulse oximeter can calculate the degree of oxygen saturation within one percent of directly measured blood oxygen, Because of their portability and speed, pulse oximeters are very useful for pilots operating in non-pressurized aircraft above 12,500' where supplemental oxygen is required, A pulse oximeter permits crew-members and passengers of an aircraft to evaluate their actual need for supplemental oxygen [, Remember, as oxygen saturation drops below 90%, you've entered the first stages of, Pilots must always check aircraft oxygen systems for accessibility inflight and operational function.
Sitemap 33
 The masks at the pilot stations will incorporate microphones to allow internal and external communications.
The masks at the pilot stations will incorporate microphones to allow internal and external communications.  No matter which type of continuous flow system you use, you'll have the choice of a nasal cannula or a rebreather mask. A regulator is installed to reduce storage cylinder pressure to a usable level. Above 41,000', the regulations of most states require that one pilot wear an oxygen mask at all times, even when quick donning masks are fitted. The aerox Quick Comfort series diluter demand mask comes standard with an electret microphone and an inflatable Quick Comfort head harness. Depending upon the aircraft type, regulators can be constant flow or diluter-demand. Aerox 4110-712 Series Oxygen Mask FAA-TSO, MH E-Z Breathe II Boom Cannula Eds For Pulse Demand, Aerox High Duration Aviation Oxygen Systems. Quiz: 6 Questions To See How Much You Know About Approach Charts, How To Plan Your Arrival At An Unfamiliar Airport, When Can You Go Below MDA Or DA On An Instrument Approach? The higher the altitude, the lower theTime of Useful Consciousness: This article describes the systems onboard commercial transport aircraft designed to supply supplemental oxygen to crew and passengers when required to sustain life. Quiz: Can You Answer These 6 Instrument Checkride Questions? Item qualifies for free ground shipping. This system uses a face-tight seal to ensure cabin air doesn't unintentionally mix into the mask. You don't need to wear a mask while flying single-pilot under FAR Part 91 as long as the cabin altitude stays at or below 35,000 feet. After you inhale air into your lungs, atmospheric pressure forces oxygen through your lungs' membranes and into your bloodstream. Re-breather masks are limited to 25,000 feet. If you're flying something that can get higher, you'll probably have a "diluter demand" system. : Boldmethod Live, How To Find Cloud Top Heights For An IFR Flight: Boldmethod Live, Setting Up The Perfect VFR Arrival To An Airport: Boldmethod Live, 8 Tips For Keeping Your Logbooks Clean, Professional, And Interview-Ready, 6 Questions You Should Be Prepared To Answer During Your CFI Interview, Why Calling 'Go-Around' Is An Action, Not A Decision Point, How To Pick The Best Flight School For You, Fatigued Flight Crew Misses Two Altitude Restrictions On Departure. Would You Go?
No matter which type of continuous flow system you use, you'll have the choice of a nasal cannula or a rebreather mask. A regulator is installed to reduce storage cylinder pressure to a usable level. Above 41,000', the regulations of most states require that one pilot wear an oxygen mask at all times, even when quick donning masks are fitted. The aerox Quick Comfort series diluter demand mask comes standard with an electret microphone and an inflatable Quick Comfort head harness. Depending upon the aircraft type, regulators can be constant flow or diluter-demand. Aerox 4110-712 Series Oxygen Mask FAA-TSO, MH E-Z Breathe II Boom Cannula Eds For Pulse Demand, Aerox High Duration Aviation Oxygen Systems. Quiz: 6 Questions To See How Much You Know About Approach Charts, How To Plan Your Arrival At An Unfamiliar Airport, When Can You Go Below MDA Or DA On An Instrument Approach? The higher the altitude, the lower theTime of Useful Consciousness: This article describes the systems onboard commercial transport aircraft designed to supply supplemental oxygen to crew and passengers when required to sustain life. Quiz: Can You Answer These 6 Instrument Checkride Questions? Item qualifies for free ground shipping. This system uses a face-tight seal to ensure cabin air doesn't unintentionally mix into the mask. You don't need to wear a mask while flying single-pilot under FAR Part 91 as long as the cabin altitude stays at or below 35,000 feet. After you inhale air into your lungs, atmospheric pressure forces oxygen through your lungs' membranes and into your bloodstream. Re-breather masks are limited to 25,000 feet. If you're flying something that can get higher, you'll probably have a "diluter demand" system. : Boldmethod Live, How To Find Cloud Top Heights For An IFR Flight: Boldmethod Live, Setting Up The Perfect VFR Arrival To An Airport: Boldmethod Live, 8 Tips For Keeping Your Logbooks Clean, Professional, And Interview-Ready, 6 Questions You Should Be Prepared To Answer During Your CFI Interview, Why Calling 'Go-Around' Is An Action, Not A Decision Point, How To Pick The Best Flight School For You, Fatigued Flight Crew Misses Two Altitude Restrictions On Departure. Would You Go?  The total number of oxygen dispensing units shall exceed the number of passenger and cabin crew seats by at least 10 per cent.
The total number of oxygen dispensing units shall exceed the number of passenger and cabin crew seats by at least 10 per cent.  For aircraft which routinely fly above 25,000', masks are generally of the "quick-donning" variety. In some cases, you'll actually dial an altitude into the regulator. In non-pressurised aircraft which routinely fly above 10,000', passenger oxygen is typically provided by either a fixed or a portable system. Pressurised aircraft which have a certified maximum altitude of 25,000' or less do not require passenger oxygen systems subject to the aircraft being able to descend to 13,000' or below within 4 minutes of loss of pressurisation. While we can't be sure it's a factor in either of the two accidents, hypoxia's a likely suspect. Airlines make a point during their safety presentation of pointing out that the bag may not inflate as, in the past, lack of bag inflation has lead some passengers to believe that their mask was not working and to remove it resulting in. Consult the appropriate documentation provided by the aircraftState of Registryfor specific criteria. But few learn about the different types of oxygen systems. As you climb, atmospheric pressure decreases, and the amount of oxygen forced into your blood also decreases. Oxygen for the use of the flight deck occupants is normally stored as pressurised gas in one or more tanks or cylinders.
For aircraft which routinely fly above 25,000', masks are generally of the "quick-donning" variety. In some cases, you'll actually dial an altitude into the regulator. In non-pressurised aircraft which routinely fly above 10,000', passenger oxygen is typically provided by either a fixed or a portable system. Pressurised aircraft which have a certified maximum altitude of 25,000' or less do not require passenger oxygen systems subject to the aircraft being able to descend to 13,000' or below within 4 minutes of loss of pressurisation. While we can't be sure it's a factor in either of the two accidents, hypoxia's a likely suspect. Airlines make a point during their safety presentation of pointing out that the bag may not inflate as, in the past, lack of bag inflation has lead some passengers to believe that their mask was not working and to remove it resulting in. Consult the appropriate documentation provided by the aircraftState of Registryfor specific criteria. But few learn about the different types of oxygen systems. As you climb, atmospheric pressure decreases, and the amount of oxygen forced into your blood also decreases. Oxygen for the use of the flight deck occupants is normally stored as pressurised gas in one or more tanks or cylinders.  Portable systems consist of a storage tank, a regulator and one or more passenger masks. Fax: 800-329-3020, West - Corona, CA
Quiz: Could You Handle These 6 Multi-Engine Failures? An operator shall ensure that passengers are made familiar with the location and use of: d) oxygen dispensing equipment, if the provision of oxygen for the use of passengers is prescribed An aeroplane intended to be operated at flight altitudes at which the atmospheric pressure is less than 700 hPa (see Note 1) in personnel compartments shall be equipped with oxygen storage and dispensing apparatus, A flight to be operated at flight altitudes at which the atmospheric pressure in personnel compartments will be less than 700 hPa shall not be commenced unless sufficient stored breathing oxygen is carried to supply: a) all crew members and 10 per cent of the passengers for any period in excess of 30 minutes that the pressure in compartments occupied by them will be between 700 hPa and 620 hPa; and b) the crew and passengers for any period that the atmospheric pressure in compartments occupied by them will be less than 620 hPa. The percentage of oxygen in the air doesn't change - it's still 21 percent. At altitudes lower than the designed optimum altitude, it will provide more oxygen than is actually required. There are three main types of oxygen systems to keep you safe - and all are meant for different altitudes. IFR Cross Country Into Low Ceilings And Scattered Storms, How To Circle-To-Land From An Instrument Approach, How To Time Your Flare For A Perfect Landing, How To Land With An Asymmetric Flap Failure, 7 Factors Every Pilot Should Consider Before Flying Around Thunderstorms, How To Fly An Approach To Landing Through Turbulence, Solo Endorsements: Understanding Basic Solo Requirements, Solo Endorsements: Understanding Solo Cross-Country Requirements, The Difference Between Decision Altitude (DA) and Decision Height (DH). source: Cabin Decompression and Hypoxia by Mark Wolff, PIA Air Safety Publication, 2006. Combine with 5110-100 Aerox Smoke Goggles and portable bottle for a standalone emergency kit! Since it automatically mixes oxygen and air only as you inhale, a diluter-demand system generally lasts longer than continuous flow. For pressurised aircraft which are certified to operate above 25,000', emergency oxygen equipment must be available. But, most systems are designed to keep you safe up to 25,000 feet. Copyright 2022 CFI Notebook, All rights reserved. Either way, the operation is simple. The most basic - and inexpensive - version pushes a standard rate of oxygen to each mask. Note 2:National or Regional Authoritiesuse the ICAO guidance as the basis for their regulations. Not a good idea. As you climb and decrease blood-oxygen, you'll eventually get hypoxic, pass out, and drone off unconscious until you run out of gas.
Portable systems consist of a storage tank, a regulator and one or more passenger masks. Fax: 800-329-3020, West - Corona, CA
Quiz: Could You Handle These 6 Multi-Engine Failures? An operator shall ensure that passengers are made familiar with the location and use of: d) oxygen dispensing equipment, if the provision of oxygen for the use of passengers is prescribed An aeroplane intended to be operated at flight altitudes at which the atmospheric pressure is less than 700 hPa (see Note 1) in personnel compartments shall be equipped with oxygen storage and dispensing apparatus, A flight to be operated at flight altitudes at which the atmospheric pressure in personnel compartments will be less than 700 hPa shall not be commenced unless sufficient stored breathing oxygen is carried to supply: a) all crew members and 10 per cent of the passengers for any period in excess of 30 minutes that the pressure in compartments occupied by them will be between 700 hPa and 620 hPa; and b) the crew and passengers for any period that the atmospheric pressure in compartments occupied by them will be less than 620 hPa. The percentage of oxygen in the air doesn't change - it's still 21 percent. At altitudes lower than the designed optimum altitude, it will provide more oxygen than is actually required. There are three main types of oxygen systems to keep you safe - and all are meant for different altitudes. IFR Cross Country Into Low Ceilings And Scattered Storms, How To Circle-To-Land From An Instrument Approach, How To Time Your Flare For A Perfect Landing, How To Land With An Asymmetric Flap Failure, 7 Factors Every Pilot Should Consider Before Flying Around Thunderstorms, How To Fly An Approach To Landing Through Turbulence, Solo Endorsements: Understanding Basic Solo Requirements, Solo Endorsements: Understanding Solo Cross-Country Requirements, The Difference Between Decision Altitude (DA) and Decision Height (DH). source: Cabin Decompression and Hypoxia by Mark Wolff, PIA Air Safety Publication, 2006. Combine with 5110-100 Aerox Smoke Goggles and portable bottle for a standalone emergency kit! Since it automatically mixes oxygen and air only as you inhale, a diluter-demand system generally lasts longer than continuous flow. For pressurised aircraft which are certified to operate above 25,000', emergency oxygen equipment must be available. But, most systems are designed to keep you safe up to 25,000 feet. Copyright 2022 CFI Notebook, All rights reserved. Either way, the operation is simple. The most basic - and inexpensive - version pushes a standard rate of oxygen to each mask. Note 2:National or Regional Authoritiesuse the ICAO guidance as the basis for their regulations. Not a good idea. As you climb and decrease blood-oxygen, you'll eventually get hypoxic, pass out, and drone off unconscious until you run out of gas.  Quick Donning High-Altitude Diluter Demand Mask, Oxygen Filling Adapters and Filling Systems, Oxygen Bottles and Installed Oxygen Systems, 4110-155 Stowage Cup for Diluter Demand Mask, 5110-100 Aerox Smoke Goggles with tear shield. The bands are adjustable to accomodate passengers of different sizes. You can find portable continuous flow systems, and many light turbocharged aircraft have them built in. But, before you get into masks, you should understand what they're trying to do. This is exhausting - it takes a significant amount of force to exhale, you'll be tired after several hours on a pressure-demand system. Given that oxygen can be a hazardous chemical in the aviation environment, Preventative safety measures further include the wear of a, Additional considerations for other operations, including. What do you do if your equipment malfunctions? Other oxygen sources carried on pressurised commercial aircraft include supplemental oxygen tank and masks units for medical use and oxygen generator equipped smoke hoods for crew use in the event that it is necessary to fight an on board fire. An easy acronym to remember how is "PRICE: Before servicing any aircraft with oxygen, consult the specific aircraft service manual to determine the type of equipment required and procedures to be used, Observe precautions whenever servicing aircraft oxygen systems, Oxygen system servicing should be accomplished only when the aircraft is outside of the hangars, Personal cleanliness and good housekeeping are imperative when working with oxygen, Oxygen under pressure and petroleum products create spontaneous results when in contact with each other, Service people should be certain to wash dirt, oil, and grease (including lip salves and hair oil) from their hands and tools before working around oxygen equipment, Aircraft with permanently installed oxygen tanks usually require two persons to accomplish servicing of the system, One should remain at the service equipment control valves, with the others located where he or she can observe the aircraft system pressure gauges, Oxygen system servicing is not recommended during aircraft fueling operations or while other work is performed that could provide a source of ignition, Oxygen system servicing while passengers are on board the aircraft is not recommended, A pilot or passenger who intends to fly after scuba diving should allow the body sufficient time to rid itself of excess nitrogen absorbed during diving, Decompression sickness can occur from evolved gas creating a serious in-flight emergency, The recommended waiting time before going to flight altitudes of up to 8,000 feet is at least 12 hours after diving which has not required controlled ascent (non-decompression stop diving), and at least 24 hours after diving which has required controlled ascent (decompression stop diving), The waiting time before going to flight altitudes above 8,000 feet should be at least 24 hours after any SCUBA dive, These recommended altitudes are actual flight altitudes above mean sea level (AMSL) and not pressurized cabin altitudes, This takes into consideration the risk of decompression of the aircraft during flight, Note that while the percentage of oxygen in the atmosphere does not decrease, pressure for the body to absorb it does, necessitating supplemental oxygen, Note the connection between supplemental oxygen and, These rules are in place because others have died from it, At night, especially when tired, these effects may occur as low as 5,000 feet, Therefore, for optimum protection, pilots are encouraged to use supplemental oxygen above 10,000 feet cabin altitude during the day and above 5,000 feet at night, While subjective, oxygen use when operating near the required altitudes for it may also improve alertness and therefore decision making, Realize that while operating near, but below, altitudes requiring oxygen, passengers may still find themselves experiencing distress without it. Quiz: Do You Know These 6 Light Gun Signals? Please note, Aircraft Spruce's personnel are not certified aircraft mechanics and can only provide general support and ideas, which should not be relied upon or implemented in lieu of consulting an A&P or other qualified technician. | Privacy Policy | Terms of Service | Sitemap | Patreon | Contact, Private pilot supplemental oxygen system airman certification standards, Aeronautical Information Manual (8-1-2) Effects of Altitude, Federal Aviation Administration - Oxygen Equipment Use in General Aviation Operations, Federal Aviation Administration - Pilot/Controller Glossary, Federal Aviation Regulations (91.211) Supplemental Oxygen, Flying and Diving - A Unique Health Concern, Pilot Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge (6-34) Oxygen Systems, Supplemental oxygen provides pilot's operating at high altitudes to counteract the effect of decreasing pressure, particularly hypoxia, Operations at higher altitudes will drive the, Aircraft designed to operate at higher altitudes will normally have an oxygen generation system, Aircraft designed to operate at low altitudes will normally have a portable oxygen system. Select the mask size, hose length, and oxygen connection below. An aeroplane intended to be operated at flight altitudes at which the atmospheric pressure is less than 376 hPa or which, if operated at flight altitudes at which the atmospheric pressure is more than 376 hPa , cannot descend safely within four minutes to a flight altitude at which the atmospheric pressure is equal to 620 hPa shall be provided with automatically deployable oxygen equipment. The emergency oxygen supply must last a minimum of 10 minutes. But, at 18,000 feet, the atmospheric pressure is half that of sea-level. The altitude compensating continuous-flow system automatically adjusts the oxygen flow rate as you climb or descend.
Quick Donning High-Altitude Diluter Demand Mask, Oxygen Filling Adapters and Filling Systems, Oxygen Bottles and Installed Oxygen Systems, 4110-155 Stowage Cup for Diluter Demand Mask, 5110-100 Aerox Smoke Goggles with tear shield. The bands are adjustable to accomodate passengers of different sizes. You can find portable continuous flow systems, and many light turbocharged aircraft have them built in. But, before you get into masks, you should understand what they're trying to do. This is exhausting - it takes a significant amount of force to exhale, you'll be tired after several hours on a pressure-demand system. Given that oxygen can be a hazardous chemical in the aviation environment, Preventative safety measures further include the wear of a, Additional considerations for other operations, including. What do you do if your equipment malfunctions? Other oxygen sources carried on pressurised commercial aircraft include supplemental oxygen tank and masks units for medical use and oxygen generator equipped smoke hoods for crew use in the event that it is necessary to fight an on board fire. An easy acronym to remember how is "PRICE: Before servicing any aircraft with oxygen, consult the specific aircraft service manual to determine the type of equipment required and procedures to be used, Observe precautions whenever servicing aircraft oxygen systems, Oxygen system servicing should be accomplished only when the aircraft is outside of the hangars, Personal cleanliness and good housekeeping are imperative when working with oxygen, Oxygen under pressure and petroleum products create spontaneous results when in contact with each other, Service people should be certain to wash dirt, oil, and grease (including lip salves and hair oil) from their hands and tools before working around oxygen equipment, Aircraft with permanently installed oxygen tanks usually require two persons to accomplish servicing of the system, One should remain at the service equipment control valves, with the others located where he or she can observe the aircraft system pressure gauges, Oxygen system servicing is not recommended during aircraft fueling operations or while other work is performed that could provide a source of ignition, Oxygen system servicing while passengers are on board the aircraft is not recommended, A pilot or passenger who intends to fly after scuba diving should allow the body sufficient time to rid itself of excess nitrogen absorbed during diving, Decompression sickness can occur from evolved gas creating a serious in-flight emergency, The recommended waiting time before going to flight altitudes of up to 8,000 feet is at least 12 hours after diving which has not required controlled ascent (non-decompression stop diving), and at least 24 hours after diving which has required controlled ascent (decompression stop diving), The waiting time before going to flight altitudes above 8,000 feet should be at least 24 hours after any SCUBA dive, These recommended altitudes are actual flight altitudes above mean sea level (AMSL) and not pressurized cabin altitudes, This takes into consideration the risk of decompression of the aircraft during flight, Note that while the percentage of oxygen in the atmosphere does not decrease, pressure for the body to absorb it does, necessitating supplemental oxygen, Note the connection between supplemental oxygen and, These rules are in place because others have died from it, At night, especially when tired, these effects may occur as low as 5,000 feet, Therefore, for optimum protection, pilots are encouraged to use supplemental oxygen above 10,000 feet cabin altitude during the day and above 5,000 feet at night, While subjective, oxygen use when operating near the required altitudes for it may also improve alertness and therefore decision making, Realize that while operating near, but below, altitudes requiring oxygen, passengers may still find themselves experiencing distress without it. Quiz: Do You Know These 6 Light Gun Signals? Please note, Aircraft Spruce's personnel are not certified aircraft mechanics and can only provide general support and ideas, which should not be relied upon or implemented in lieu of consulting an A&P or other qualified technician. | Privacy Policy | Terms of Service | Sitemap | Patreon | Contact, Private pilot supplemental oxygen system airman certification standards, Aeronautical Information Manual (8-1-2) Effects of Altitude, Federal Aviation Administration - Oxygen Equipment Use in General Aviation Operations, Federal Aviation Administration - Pilot/Controller Glossary, Federal Aviation Regulations (91.211) Supplemental Oxygen, Flying and Diving - A Unique Health Concern, Pilot Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge (6-34) Oxygen Systems, Supplemental oxygen provides pilot's operating at high altitudes to counteract the effect of decreasing pressure, particularly hypoxia, Operations at higher altitudes will drive the, Aircraft designed to operate at higher altitudes will normally have an oxygen generation system, Aircraft designed to operate at low altitudes will normally have a portable oxygen system. Select the mask size, hose length, and oxygen connection below. An aeroplane intended to be operated at flight altitudes at which the atmospheric pressure is less than 376 hPa or which, if operated at flight altitudes at which the atmospheric pressure is more than 376 hPa , cannot descend safely within four minutes to a flight altitude at which the atmospheric pressure is equal to 620 hPa shall be provided with automatically deployable oxygen equipment. The emergency oxygen supply must last a minimum of 10 minutes. But, at 18,000 feet, the atmospheric pressure is half that of sea-level. The altitude compensating continuous-flow system automatically adjusts the oxygen flow rate as you climb or descend.  When you think of an oxygen mask, you probably either think of the thing hanging around a fighter pilot's neck, or one of those little yellow dixie cups that drop from the overhead panels of an airliner. Let's take a look.
When you think of an oxygen mask, you probably either think of the thing hanging around a fighter pilot's neck, or one of those little yellow dixie cups that drop from the overhead panels of an airliner. Let's take a look.  At low altitudes, it pushes too much oxygen. As an example, at 8000', the regulator might send 100% ambient air to the mask whereas at 41000', it would provide 100% oxygen. For diluter-demand systems, selectors for normal, 100% and positive pressure maybe incorporated into the mask itself. If the aircraft is not capable of achieving the descent profile or the route structure does not allow the descent due to terrain, an oxygen system must be fitted in the aircraft as per the provisions which apply to aircraft which are certified to fly at higher altitudes (above 25,000'). Supply Press Range: 55 to 70 Psi * (0.37 to 0.48 Mpa), Operating Temp Range: +20 0 to +1200 F ** (-290 to +490C). When installed, diluter-demand regulators will be located at each crew position. 2021 All Rights Reserved. Please note other excluded items on the same order may incur a freight charge.
At low altitudes, it pushes too much oxygen. As an example, at 8000', the regulator might send 100% ambient air to the mask whereas at 41000', it would provide 100% oxygen. For diluter-demand systems, selectors for normal, 100% and positive pressure maybe incorporated into the mask itself. If the aircraft is not capable of achieving the descent profile or the route structure does not allow the descent due to terrain, an oxygen system must be fitted in the aircraft as per the provisions which apply to aircraft which are certified to fly at higher altitudes (above 25,000'). Supply Press Range: 55 to 70 Psi * (0.37 to 0.48 Mpa), Operating Temp Range: +20 0 to +1200 F ** (-290 to +490C). When installed, diluter-demand regulators will be located at each crew position. 2021 All Rights Reserved. Please note other excluded items on the same order may incur a freight charge.  And, how can you tell if you're hypoxic?
And, how can you tell if you're hypoxic?  For new airline pilots and those upgrading to advanced aircraft, VNAV is one of the biggest automation hurdles to understand. Overhaul: Aerox recommends every 3 years. The mask could be of the "full face" variety incorporating smoke goggles or a "mouth and nose" type mask with smoke goggles available separately. Some aircraft utilize cylinders of pressurised oxygen to meet this requirement but most types are fitted with.
For new airline pilots and those upgrading to advanced aircraft, VNAV is one of the biggest automation hurdles to understand. Overhaul: Aerox recommends every 3 years. The mask could be of the "full face" variety incorporating smoke goggles or a "mouth and nose" type mask with smoke goggles available separately. Some aircraft utilize cylinders of pressurised oxygen to meet this requirement but most types are fitted with.  If a LOX system is installed, a LOX converter, which facilitates the transformation of the oxygen from a liquid to a gaseous state, will also be installed. Quiz: Do You Know These 5 Common IFR Phrases? There are a variety of different oxygen systems and delivery methods available to general and commercial aviation, including: Generally used on large aircraft in case of an emergency to provide a 10 minute supply of oxygen, Activated by a lanyard on the oxygen mask, as the user pulls the mask to their face, a chemical reaction with sodium chlorate is triggered, Once this system is activated, it must burn out, requiring replacement, Chemical oxygen is lightweight and compact, No more than 0.005 ml of water per 1 liter of oxygen = 99.5% O, Portable gaseous oxygen system provides oxygen when required for aircraft which lack an integral oxygen system, These systems are used for passengers or crew members when the aircraft oxygen systems services only the pilot and copilot, or when the duties of the crew require them to move about the aircraft, A portable unit weighs approximately 20 pounds and typically consists of: lightweight steel oxygen cylinder (usually 1800 Pounds per Square Inch (PSI), capacity vary), associated plumbing, combined flow control/reducing valve pressure gauge, and a breathing mask and connecting hose, On-Board Oxygen Generating System, or OBOGS, converts engine compressor bleed air to oxygen-rich breathing air and pressurized air for at the correct pressure and temperature, OBOGS provides a continuous supply of breathing air for crew while the engine is operating, Components consist of a heat exchanger, concentrator, regulator, and associated plumbing, Liquid oxygen systems, or LOX, is used in some jet aircraft because LOX storage occupies less space and weigh less than those used for gaseous oxygen, LOX systems typically consists of converters, check valves and manifolds, oxygen heat exchanger, oxygen/vent airflow control panel, liquid quantity indicator, and a breathing mask with connecting hoses, There are numerous types and designs of oxygen masks in use, The most critical factor in oxygen mask use is to ensure the masks and oxygen system are compatible, Crew masks are fitted to the user's face with a minimum of leakage and usually contain a microphone, Most masks are the oronasal type, which covers only the mouth and nose, A passenger mask may be a simple, cup-shaped rubber molding sufficiently flexible to prevent individual fitting, It may have a simple elastic head strap, or the passenger may hold it to his or her face, All oxygen masks should be clean to reduce the danger of infection and prolong the life of the mask, To clean the mask, wash it with a mild soap and water solution and rinse it with clear water, If a containing a microphone, use a clean swab, instead of running water, to wipe off the soapy solution, A gauze pad that has been soaked in a water solution of Merthiolate can be used to swab out the mask, This solution used should contain a one-fifth teaspoon of Merthiolate per quart of water, Wipe the mask with a clean cloth and air dry, Both pressure and diluter-demand systems use a diaphragm operated demand valve, which opens when suction from inhalation is present, A cannula is an ergonomic piece of plastic tubing that runs under the nose and is often used to administer oxygen in non-pressurized aircraft [, Cannulas are typically more comfortable than masks and can be used up to 18,000', Many cannulas have a flow meter in the line, and if equipped, a periodic check of the green flow detector should be part of a pilot's regular scan, Passenger aircraft generally utilize continuous-flow oxygen systems, The passenger mask typically has a reservoir bag, which collects oxygen from the continuous-flow oxygen system when the mask user is exhaling, The oxygen collected in the reservoir bag allows a higher aspiratory flow rate during the inhalation cycle, which reduces the amount of air dilution, Ambient air is added to the supplied oxygen during inhalation after the reservoir bag oxygen supply is depleted, Portable electrical pulse-demand oxygen systems deliver oxygen by detecting an individual's inhalation effort and provide oxygen flow during the initial portion of inhalation, Pulse demand systems do not waste oxygen during the breathing cycle because oxygen only delivers during inhalation, Compared to continuous-flow systems, the pulse-demand method of oxygen delivery can reduce the amount of oxygen needed by 50-85%, Most pulse-demand oxygen systems also incorporate an internal barometer that automatically compensates for changes in altitude by increasing the amount of oxygen delivered for each pulse as altitude is increased [, These systems can be either built in or portable, Check valves allow for exhaled air to exit the mask at high altitudes completely, General flow rates are 120 liters per hour for crew and 90 liters per hour for passengers, Diluter-demand oxygen systems supply oxygen only when the user inhales through the mask, An auto-mix lever allows the regulators to automatically mix cabin air and oxygen or supply 100% oxygen, depending on the altitude, The demand mask provides a tight seal over the face to prevent dilution with outside air, A pilot who has a beard or mustache should ensure it will not interfere with the sealing of the oxygen mask, Pressure-demand oxygen systems are similar to diluter demand oxygen equipment, except that oxygen is supplied to the mask under pressure at cabin altitudes above 34,000', Pressure-demand regulators create airtight and oxygen-tight seals, but they also provide a positive pressure application of oxygen to the mask facepiece that allows the user's lungs to pressurize with oxygen, Pressure-demand is used above 40,000' because even with 100% O, Some systems may have a pressure-demand mask with the regulator attached directly to the mask rather than mounted on the instrument panel or other area within the flight deck, The mask-mounted regulator eliminates the problem of a long hose that must be purged of air before 100% oxygen begins flowing into the mask, Aircraft oxygen stores in high-pressure system containers of 1,800-2,200 PSI, When the ambient temperature surrounding an oxygen cylinder decreases, the pressure within that cylinder decreases because pressure varies directly with temperature if the volume of a gas remains constant, If indicated pressure on a supplemental oxygen cylinder drops, there is no reason to suspect depletion of the oxygen supply, which has compressed due to storage of the containers in an unheated area of the aircraft, High-pressure oxygen containers have markings with the psi tolerance (i.e., 1,800 psi) before filling the container to that pressure, Service containers with aviation oxygen only, which is 100% pure oxygen, Industrial oxygen is not intended for breathing and may contain impurities, and facepiece oxygen masks may contain water vapor that can freeze in the regulator when exposed to cold temperatures, To assure safety, pilots should do periodic inspection and servicing of the oxygen system, Oxygen is an oxidizer, supporting combustion, and an extremely hazardous material in the aviation environment, Acting as a catalyst, small sparks or fires in the presence of combustibles such as oils, fuels, and other chemicals can quickly grow, Purge hoses before coupling to aircraft filler valves to avoid contamination, Containers need to be filled in a controlled manner to avoid overheating, Keep oil and grease away from oxygen equipment, including tools and protective clothing to avoid contamination, Use spark-free tools (brass) when servicing oxygen systems, Do not open valves of an oxygen system or cylinder when a flame, electrical arc, or any other source of ignition is in the immediate area, Take extreme caution not to touch implements containing liquid oxygen without gloves due to the extremely low temperature, Use protective clothing when working with LOX including gloves, coveralls, face shields, and LOX boots, Never seal or cap the vent port of a LOX system, Vent design ensures sufficient flow capacity to carry away LOX that may escape, The expansion ratio of liquid oxygen is 862 to 11-liquid oxygen at atmospheric pressure will a generate pressure of up to 12,000 PSI, If allowed to evaporate in a sealed container or system which has no relief provisions, LOX could cause an explosion, Never saturate cloth, wood, grease, oil paint, or tar with LOX, LOX by itself will not burn, but mixing it with any material will cause the LOX to boil and splash violently with possible combustion, A pulse oximeter is a device that measures the amount of oxygen in an individual's blood, in addition to heart rate, This non-invasive device measures the color changes that red blood cells undergo when they become saturated with oxygen, By transmitting a special light beam through a fingertip to evaluate the color of the red cells, a pulse oximeter can calculate the degree of oxygen saturation within one percent of directly measured blood oxygen, Because of their portability and speed, pulse oximeters are very useful for pilots operating in non-pressurized aircraft above 12,500' where supplemental oxygen is required, A pulse oximeter permits crew-members and passengers of an aircraft to evaluate their actual need for supplemental oxygen [, Remember, as oxygen saturation drops below 90%, you've entered the first stages of, Pilots must always check aircraft oxygen systems for accessibility inflight and operational function.
If a LOX system is installed, a LOX converter, which facilitates the transformation of the oxygen from a liquid to a gaseous state, will also be installed. Quiz: Do You Know These 5 Common IFR Phrases? There are a variety of different oxygen systems and delivery methods available to general and commercial aviation, including: Generally used on large aircraft in case of an emergency to provide a 10 minute supply of oxygen, Activated by a lanyard on the oxygen mask, as the user pulls the mask to their face, a chemical reaction with sodium chlorate is triggered, Once this system is activated, it must burn out, requiring replacement, Chemical oxygen is lightweight and compact, No more than 0.005 ml of water per 1 liter of oxygen = 99.5% O, Portable gaseous oxygen system provides oxygen when required for aircraft which lack an integral oxygen system, These systems are used for passengers or crew members when the aircraft oxygen systems services only the pilot and copilot, or when the duties of the crew require them to move about the aircraft, A portable unit weighs approximately 20 pounds and typically consists of: lightweight steel oxygen cylinder (usually 1800 Pounds per Square Inch (PSI), capacity vary), associated plumbing, combined flow control/reducing valve pressure gauge, and a breathing mask and connecting hose, On-Board Oxygen Generating System, or OBOGS, converts engine compressor bleed air to oxygen-rich breathing air and pressurized air for at the correct pressure and temperature, OBOGS provides a continuous supply of breathing air for crew while the engine is operating, Components consist of a heat exchanger, concentrator, regulator, and associated plumbing, Liquid oxygen systems, or LOX, is used in some jet aircraft because LOX storage occupies less space and weigh less than those used for gaseous oxygen, LOX systems typically consists of converters, check valves and manifolds, oxygen heat exchanger, oxygen/vent airflow control panel, liquid quantity indicator, and a breathing mask with connecting hoses, There are numerous types and designs of oxygen masks in use, The most critical factor in oxygen mask use is to ensure the masks and oxygen system are compatible, Crew masks are fitted to the user's face with a minimum of leakage and usually contain a microphone, Most masks are the oronasal type, which covers only the mouth and nose, A passenger mask may be a simple, cup-shaped rubber molding sufficiently flexible to prevent individual fitting, It may have a simple elastic head strap, or the passenger may hold it to his or her face, All oxygen masks should be clean to reduce the danger of infection and prolong the life of the mask, To clean the mask, wash it with a mild soap and water solution and rinse it with clear water, If a containing a microphone, use a clean swab, instead of running water, to wipe off the soapy solution, A gauze pad that has been soaked in a water solution of Merthiolate can be used to swab out the mask, This solution used should contain a one-fifth teaspoon of Merthiolate per quart of water, Wipe the mask with a clean cloth and air dry, Both pressure and diluter-demand systems use a diaphragm operated demand valve, which opens when suction from inhalation is present, A cannula is an ergonomic piece of plastic tubing that runs under the nose and is often used to administer oxygen in non-pressurized aircraft [, Cannulas are typically more comfortable than masks and can be used up to 18,000', Many cannulas have a flow meter in the line, and if equipped, a periodic check of the green flow detector should be part of a pilot's regular scan, Passenger aircraft generally utilize continuous-flow oxygen systems, The passenger mask typically has a reservoir bag, which collects oxygen from the continuous-flow oxygen system when the mask user is exhaling, The oxygen collected in the reservoir bag allows a higher aspiratory flow rate during the inhalation cycle, which reduces the amount of air dilution, Ambient air is added to the supplied oxygen during inhalation after the reservoir bag oxygen supply is depleted, Portable electrical pulse-demand oxygen systems deliver oxygen by detecting an individual's inhalation effort and provide oxygen flow during the initial portion of inhalation, Pulse demand systems do not waste oxygen during the breathing cycle because oxygen only delivers during inhalation, Compared to continuous-flow systems, the pulse-demand method of oxygen delivery can reduce the amount of oxygen needed by 50-85%, Most pulse-demand oxygen systems also incorporate an internal barometer that automatically compensates for changes in altitude by increasing the amount of oxygen delivered for each pulse as altitude is increased [, These systems can be either built in or portable, Check valves allow for exhaled air to exit the mask at high altitudes completely, General flow rates are 120 liters per hour for crew and 90 liters per hour for passengers, Diluter-demand oxygen systems supply oxygen only when the user inhales through the mask, An auto-mix lever allows the regulators to automatically mix cabin air and oxygen or supply 100% oxygen, depending on the altitude, The demand mask provides a tight seal over the face to prevent dilution with outside air, A pilot who has a beard or mustache should ensure it will not interfere with the sealing of the oxygen mask, Pressure-demand oxygen systems are similar to diluter demand oxygen equipment, except that oxygen is supplied to the mask under pressure at cabin altitudes above 34,000', Pressure-demand regulators create airtight and oxygen-tight seals, but they also provide a positive pressure application of oxygen to the mask facepiece that allows the user's lungs to pressurize with oxygen, Pressure-demand is used above 40,000' because even with 100% O, Some systems may have a pressure-demand mask with the regulator attached directly to the mask rather than mounted on the instrument panel or other area within the flight deck, The mask-mounted regulator eliminates the problem of a long hose that must be purged of air before 100% oxygen begins flowing into the mask, Aircraft oxygen stores in high-pressure system containers of 1,800-2,200 PSI, When the ambient temperature surrounding an oxygen cylinder decreases, the pressure within that cylinder decreases because pressure varies directly with temperature if the volume of a gas remains constant, If indicated pressure on a supplemental oxygen cylinder drops, there is no reason to suspect depletion of the oxygen supply, which has compressed due to storage of the containers in an unheated area of the aircraft, High-pressure oxygen containers have markings with the psi tolerance (i.e., 1,800 psi) before filling the container to that pressure, Service containers with aviation oxygen only, which is 100% pure oxygen, Industrial oxygen is not intended for breathing and may contain impurities, and facepiece oxygen masks may contain water vapor that can freeze in the regulator when exposed to cold temperatures, To assure safety, pilots should do periodic inspection and servicing of the oxygen system, Oxygen is an oxidizer, supporting combustion, and an extremely hazardous material in the aviation environment, Acting as a catalyst, small sparks or fires in the presence of combustibles such as oils, fuels, and other chemicals can quickly grow, Purge hoses before coupling to aircraft filler valves to avoid contamination, Containers need to be filled in a controlled manner to avoid overheating, Keep oil and grease away from oxygen equipment, including tools and protective clothing to avoid contamination, Use spark-free tools (brass) when servicing oxygen systems, Do not open valves of an oxygen system or cylinder when a flame, electrical arc, or any other source of ignition is in the immediate area, Take extreme caution not to touch implements containing liquid oxygen without gloves due to the extremely low temperature, Use protective clothing when working with LOX including gloves, coveralls, face shields, and LOX boots, Never seal or cap the vent port of a LOX system, Vent design ensures sufficient flow capacity to carry away LOX that may escape, The expansion ratio of liquid oxygen is 862 to 11-liquid oxygen at atmospheric pressure will a generate pressure of up to 12,000 PSI, If allowed to evaporate in a sealed container or system which has no relief provisions, LOX could cause an explosion, Never saturate cloth, wood, grease, oil paint, or tar with LOX, LOX by itself will not burn, but mixing it with any material will cause the LOX to boil and splash violently with possible combustion, A pulse oximeter is a device that measures the amount of oxygen in an individual's blood, in addition to heart rate, This non-invasive device measures the color changes that red blood cells undergo when they become saturated with oxygen, By transmitting a special light beam through a fingertip to evaluate the color of the red cells, a pulse oximeter can calculate the degree of oxygen saturation within one percent of directly measured blood oxygen, Because of their portability and speed, pulse oximeters are very useful for pilots operating in non-pressurized aircraft above 12,500' where supplemental oxygen is required, A pulse oximeter permits crew-members and passengers of an aircraft to evaluate their actual need for supplemental oxygen [, Remember, as oxygen saturation drops below 90%, you've entered the first stages of, Pilots must always check aircraft oxygen systems for accessibility inflight and operational function.