We recommend you now use our main cable sizing application over at myCableEngineering.com. Not for use in diagnostic procedures." Calculating motor RPM, as well as other measurements like torque, voltage and power, is essential when choosing a motor for a given application.

To calculate RPM for an AC induction motor, you multiply the frequency in Hertz (Hz) by 60for the number of seconds in a minuteby two for the negative and positive pulses in a cycle. Announcing the Stacks Editor Beta release! Several other factors impact speed in DC motors, including the motors operating voltage, the strength of the magnets and the number of wire turns the armature has. When operating, monitoring, repairing or replacing a motor, its essential to understand its specifications. Asked of someone who should have learned a lot about motors including their losses, it is a question that is designed to make the student think carefully about what is being asked. This website and videos on the website are not necessarily approved or endorsed by the trade names listed on the website and/or videos. So, even when spinning at the same RPM, a larger Radius will produce larger forcesjust as a smaller Radius will produce smaller forces. LUO: Laboratory Use Only. That means that the speed of an ideal unloaded induction motor is the synchronous speed. Positive and zero sequence impedance to IEC 60609. No not at all too be honest. For your convenience, you can find the I.F.U.
.jpg)
Its important to understand the specifications of your equipment, so you can better operate and maintain it. Professional repair and maintenance services may also play an important role in helping you take full advantage of your equipments capabilities. Electrohydraulic Servo Valves & Actuators, Magnetic Starters - Disconnect Combination, East Coast Repair Facility Corporate Location, choose the right kind of motor when replacing components, (Hz x 60 x 2) / number of poles = no-load RPM, ((synchronous speed-rated full-load speed) / (synchronous speed)) x 100 = slip rating. With the development Integer number between 300 and 3600 is required! Copyright/Trademark Yes, that addresses the unasked question: "how does an ideal motor actually reach synchronous speed"? The European Union is implementing a voluntary code of practice for participants with the aim of improving the overall efficiency of data centres. Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search. @CharlesCowie what do you think the real question might be? These products are labeled "For In Vitro Diagnostic Use." Mention of the slip could be considered something thrown in to make this a trick "question." Stack Exchange network consists of 181 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers. My instructor has barely touched on motors and that subject, so I am not too confident in this part of electrical engineering. Additionally,k-factor is calculated and therefore values might differ slightly from rotor IFU. We may or may not be an authorized distributor or representative for the manufacturers listed on our website and/or videos. Unless your course has given you a definition of nominal slip that doesn't use the "ideal unloaded rotor speed" you've finished. What is the derivation for "Partial Expectation"? Typically, the manufacturer of the motor will tell you the RPM you can expect at various voltages. You then divide by the number of poles the motor has: You can also calculate the slip rating by subtracting the rated full load speed from the synchronous speed, dividing that answer by the synchronous speed and multiplying that answer by 100: Then, to find the full-load RPM, you convert the slip rating to RPM and then subtract it from the no-load RPM: The RPM of a DC motor depends on the voltage supplied to the motor.

You can also use controls to adjust the speed of a DC motor, which works by varying the voltage available to the motor. RPM stands for revolutions per minute. This is how centrifuge manufacturers will communicate and display how fast your samples are rotating around the axis of the rotor. Beckman Coulter, the stylized logo, and the Beckman Coulter product and service marks mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of Beckman Coulter, Inc. in the United States and other countries. Click here to register to use our cable sizing application. Mathematica won't validate Fresnel Integral identity. This field leads to the creation of magnetic fields in the rotor that relate to the frequency of the field in the stator. @BrianDrummond the question says "unloaded" in the pasted text.

Calculating motor speed can help you choose the right kind of motor when replacing components and help you make better repair decisions. Powerful performance, exceptional simplicity. Follow the programming instructions of your centrifuge manufacturer. Revised manuscript sent to a new referee after editor hearing back from one referee: What's the possible reason? Nevertheless, I have used the word "nominal" to mean very lightly loaded. It has to spin slightly slower than sync speed in order for a voltage to be induced in the rotor so that rotor current can flow in the squirrel cage and, produce a counteracting magnetic field (that allows a torque to develop that produces motion). Once you know what G-Force you need to spin your samples at, you can measure the radius of your centrifuge rotor and calculate the RPM using the equations provided above or by using the Nomograph found below. What technologies make it possible to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact with high performance floor model centrifuges? If you know the RPM, the equations to calculate G-Force are: In Centimeters: RCF orG-Force = 0.00001118 x Rotor Radius x (RPM), In Inches: RCF orG-Force = 0.0000284 x Rotor Radius x (RPM). I am pretty sure you have not answered what is being asked. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. speed" or have I calculated something different? If you connect a motor to a power source, the speed will increase, although this may cause your motor to experience additional wear. "I can live with doubt and uncertainty and not knowing. These products are labeled "For Research Use Only. Blood Banking Applications Using the Thermo Scientific Sorvall BP 8 and 16 and Cryofuge 8 and 16 Centrifuges, Large Volume Precipitation of Proteins with Ammonium Sulfate, Large Scale Recombinant Protein Production, Pelleting Studies with the Thermo Scientific Fiberlite F21S-8x50y Fixed-Angle Rotors (TICFGPELLETFIBER-0309), Sample Re-Mixing During Density Gradient Separations with the Thermo Scientific F21-8x50y mL Fixed Angle Rotor (TICFGSAMMIX-0309), Isolation of RNA Using the Thermo Scientific Sorvall MTX Micro-Ultracentrifuge and Rotors, Efficient Separation of Tomato Soluble Solids Using the Thermo Scientific Sorvall MTX Micro-Ultracentrifuge and S140-AT Rotor, Isolation of Plasma Membrane from Endothelial Cells Using the Thermo Scientific Sorvall MTX Micro-Ultracentrifuge and S55-A2 Rotor, Rapid Separation of Human Serum Lipoproteins, Separation of Influenza Virus Using the Thermo Scientific S50-A Fixed-Angle Rotor and Sorvall Micro-Ultracentrifuge, Nanoparticle Separations in Thermo Scientific Sorvall Micro-ultracentrifuges, Banding of Intact Bacteriophage using the Thermo Scientific S100-AT6 Ultracentrifuge Rotor, Separation of Lysosomes and Endosomes from Rat Liver Homogenate using Thermo Scientific Fiberlite Rotors, High Efficiency Differential Ultracentrifugation of Small Sample Volumes, Isolation of RNA by the Guanidine Thiocyanate (GTC) Method, Rapid, High-Volume Fractionation of Plasma Proteins, Rapid Separation of Endosomes from Lysosomes, Rapid, Single-Spin Fractionation of Serum Lipoproteins by Density Gradient Ultracentrifugation, Separation of Lipid "Rafts" by Sucrose Gradient, Traditional Methods for CsCl Isolation of Plasmid DNA, Separation of Influenza Viruses Using a Fixed-Angle Rotor Designed for Micro-Ultracentrifuges (ANCFGINFVIRUS 0110), Rapid Isolation of RNA by Guanidinium Thiocyanate/Cesium Chloride Using Thermo Scientific Fiberlite Ultracentrifuge Rotors (ANCFGRNAGUAN 1110), Purification of Glycoproteins from Bronchial Mucus Fluids (ANCFGPURGIY 1110), Rapid concentration of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater samples by ultracentrifugation for disease surveillance (Ref COL25235 0621), Lipemia removal in serum samples by centrifugation (Ref COL25221 0621), Separation of Rotavirus Using a Thermo Scientific Fiberlite Fixed Angle Rotor (TNCFGSEPROTVIRUS 1111), Sorvall LYNX Superspeed Centrifuge Series, Sorvall MTX 150 and MX Plus Micro-Ultracentrifuges, Sorvall LYNX superspeed centrifuge rotor guide, Sorvall WX+ series ultracentrifuge rotor guide, Sorvall MTX/MX+ series micro-ultracentrifuge rotor guide, Technical Note: Centri-Vue for real-time connection with select superspeed and large capacity centrifuges [EN], Case Study:Sorvall BIOS 16 Bioprocessing Centrifuge doubles biotech lab efficiency overnight, Spectroscopy, Elemental & Isotope Analysis, Preclinical to Companion Diagnostic Development, Microbiological Media and Media Additives, Gel Electrophoresis Equipment and Supplies. Thermo Fisher Scientific. Convert all small words (2-3 characters) to upper case with awk or sed. An unloaded motor is one that has nothing connected to the motor shaft. A limited liability company corporated in England. Analytical and performance characteristics are not established." G-Force = 0.00001118 x Rotor Radius x (RPM), G-Force = 0.0000284 x Rotor Radius x (RPM), RPM = sqrt(G-Force / (0.00001118 x Rotor Radius)), RPM = sqrt(G-Force / (0.0000284 x Rotor Radius)). Traditionally generation of electricity has involved rotating machines to produce alternating sinusoidal voltage and current (a.c. systems). However, even at the same RPM, the centrifugal force applied to your samples can vary as a function of the Radius of the rotor. At GlobalElectronic Services, we have extensive experience repairing and servicing a wide range of industrial equipment, including AC and DC motors, servo motors, industrial electronics, hydraulics and pneumatics and more. There are a lot of interesting two page type notes on various medium voltage topics switchgear, circuit breakers, bus systems etc. Many AC controls also have a single phase input, which enables you to run three-phase motors even if you dont have three-phase power available. To adjust the speed of a three-phase AC motor, you can adjust the frequency of the AC motors power supply using a control. If you are using a centrifuge that does not display G-Force and you are executing a protocol with one or more G-Force requirements, you will need to calculate the RPM that achieves the required G-Forces and set the centrifuge by the RPM display. with the rotor radius and the rotation speed of the centrifuge. Legal How can blood banks eliminate potential variables to ensure consistent product yield and reproducibility? Having said that, many induction motors will have a full load speed at around 90% to 95% slip; such as is depicted in this picture: -. But is this what is meant when they ask for the "ideal unloaded rotor speed" or have I calculated something different?

In this case, that would be: At 60 Hz, a motor with two poles operates at 3,600 RPM with no load and about 3,450 RPM with a load: At 60 Hz, a motor with six poles would run at 1,200 RPM under no load and at approximately 1,175 RPM loaded. Search RPM is a measurement used to describe a motors speed. You can calculate G-Forces using either inches or centimeters for the radius of the centrifuge. MathJax reference. Combining these two formulas and isolating \$N\$ we get: \$N=\frac{-120Sf}{P}+\frac{120f}{P}=\frac{-120 \cdot 0.05\cdot350 \text{Hz}}{8 \:\text{poles}}+\frac{120\cdot 350\text{Hz}}{8\:\text{poles}}=4987.50 \: \text{RPM}\$. A nominal slip of 5% (rotor unloaded as per the pasted text in the question) means that it is rotating at 5% lower than synchronous speed. For example, when revolving at 3,500 RPM, a large rotor with a radius of 15 cm will produce a maximum G-Force of 2,058 xg, while a small rotor with a radius of 5 cm will produce a maximum G-Force of 686 xg. The key words here are "ideal" and "unloaded", I have not regarded the word "nominal" to mean it has a 5% slip at full load because it would be impossible to accurately predict what slip it has when unloaded. I would express the answer as below but arbitrarily close to synch speed. Slip in an induction motor is what makes the motor capable of producing torque. ASR: Analyte Specific Reagents. In summary, you should always set your centrifuge to the correct G-Force, not by an assumed RPM. The information presented by the Intellifuge calculator should be used for estimation purposes and should be used as a reference only. Regulatory: regulatory@druckerdiagnostics.com, Drucker Diagnostics Headquarters: Port Matilda, PA16870 USA, Drucker Diagnostics Manufacturing: But I am not sure WHY induction motors have slip in the first place. DC motors can only perform at speeds rated for the amount of voltage available to it. These products are labeled "For Laboratory Use Only." In this guide, well discuss how to calculate the RPM of a motor and why its so important. To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader. By clicking Accept all cookies, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy. These reagents are labeled "Analyte Specific Reagents. LV and MV cables up to 33 kV with current capacity in accordance with BS 7671, ERA 69-30 and IEC 60502. The relationship between poles and the RPM of a motor has to do with the magnetic field produced in the stator poles. The slip is the difference between the no-load speed and the full-load speed. The Radius can be measured at the top of the specimen as the Minimum Radius, the middle of the specimen as the Average Radius, or at the bottom of the specimen as the Maximum Radius. var d = new Date(); document.getElementById("footerYear").innerHTML = d.getFullYear(); Fisher Scientific UK Ltd All rights reserved. cables from anywhere and on any device, desktop, tablet or smartphone. Most single-phase AC motors, on the other hand, arent adjustable since they plug directly into a standard outlet and use the frequency that is available. Also refer to rotor IFUs for proper tube fill volumes and for specific information and use for tubes requiring caps and spacers. Why isn't the vector field being plotted over the entire torus? In the normal load range, the slip of an induction motor is a fairly linear function of torque. RCF is positively related To learn more about what cookies are and how to manage them visit, EU Code of Conduct on Data Centres - Best Practices, Tips for a better Low Voltage Protection Discrimination Study. Sitemap. More like San Francis-go (Ep. It stands for revolutions per minute and describes the rate at which the rotor is revolving, which is the number of times the rotor shaft completes a full rotation each minute. @Andyaka I would interpret "nominal" slip to mean slip at nominal full load. These speeds are the same, even across various models and manufacturers. So that we can focus all our efforts on our new application, we have retired our myElectrical.com cable sizing calculator. Is there a difference in Earth's magnetic field between day and night? Patents document.write(new Date().getFullYear()) Beckman Coulter, Inc. All rights reserved. Fisher Scientific, Bishop Meadow Road, Loughborough, Leicestershire, LE11 5RG. RUO: Research Use Only. Why is the comparative of "sacer" not attested? Can the difference of two bounded decreasing functions oscillate? Lets take a look at some examples. That does not mean that no torque is being produced, there are still mechanical losses consisting of bearing friction and aerodynamic drag inside the motor and due to the cooling fan that may be on the end of the shaft opposite the drive end. Those losses are neglected fo an "ideal" unloaded motor. RCF = 1.118 * 10-5 * r * (rpm)2 I believe that is the intent of the question. For exact information, refer to the specific rotor instruction for use (IFU). Tip: registered users can save calculations. Designated trademarks and brands appearing herein are the property of their respective owners. The Force exerted on a sample in a centrifuge is a function of the rotation speed of the centrifuge (RPM) and the radius of the rotor. All pictures are for reference only and may not be the actual unit. How can instant rotor identification enhance productivity and safety during your centrifuge set-up and run? It only takes a minute to sign up. 2022 Global Electronic Services, Inc. All rights reserved. You may also use the equations provided above if you prefer to use the equations to the Nomograph. Tapping your forearm or hand with a finger could soon be the way you interact with gadgets. r : Rotor radius, in "cm" Our website uses cookies so that we can provide a better experience. Electrophoresis, Western Blotting and ELISA, Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry Reagents, Search online for Assays, Antibodies, Oligos, Chlorine and pH Test Kits and Test Strips. Perform custom calculations with our RPM and RCF calculator and find the g-force of your Thermo Scientific Fiberlite centrifuge rotor at any rpm. PRODUCT AVAILABILITY AND REGULATORY STATUS DEPENDS ON COUNTRY REGISTRATION PER APPLICABLE REGULATIONS for the most common brands here. I interpret "ideal unloaded rotor speed" as synchronous speed since that is the ideal speed when zero torque, internal or external. But here I would be inclined towards the 5% slip and assume by "nominal" they mean the slip when no external load applied since it still takes force to turn an unloaded rotor and therefore requires slip. To achieve the desired RPM, you can then adjust the voltage according to the guidelines. The Earth is teleported into interstellar space for 5 minutes. Use MathJax to format equations. Our software is the only cloud-based solution and has been built from the ground up to be fully responsive - meaning you can access your Sales: sales@druckerdiagnostics.com Which Marvel Universe is this Doctor Strange from? What is the slip factor for an induction generator in an island network? 2000-
rev2022.7.29.42699. A reasonable full-load speed for a 60 Hz, four-pole motor would be 1,725 RPM. What happens? In this case, you can easily set the centrifuge by G-Force without doing the calculations. For a 60 Hz system with four poles, the calculations to determine RPM would be: The amount of slip varies slightly based on the motors design. 2022 Community Moderator Election Results. Due to current global supply chain challenges we are experiencing extended and erratic lead times for, Air Particle Counters for Cleanroom and Environmental Monitoring, Cell Counters, Sizers and Media Analyzers, Navios EX Powerful, Dependable Flow Cytometer, Biomek NGeniuS Next Generation Library Prep System, HIAC 9703+ Pharmaceutical Particle Counter, Shop Conjugated Antibodies, Antibody Cocktails, Lysing, Fixative, and Permeabilizating Reagents, Plate Loader Options for the CytoFLEX Platform, Customer Relations for Beckman Coulter Life Sciences. Measurable and meaningful skill levels for developers, San Francisco? How gamebreaking is this magic item that can reduce casting times? According to Andy aka's it seems like the nominal slip tells how much lower the rotor speed is compared to the synchronous speed. Carl, you have thought enough about the question to doubt that you understand it. The speed of a given motor depends on the line frequency of the power supply, rather than the voltage, as well as the number of poles it has. In most engineering contexts, "ideal" means neglecting all losses and characteristics that make things complicated. The listed regulatory status for products correspond to one of the below: Privacy Statement But is this what is meant when they ask for the "ideal unloaded rotor One crucial measurement is revolutions per minute, or RPM, which describes the speed of a motor. Carrying out a protection system discrimination study is critical to ensure the correct functioning of the electrical system in the event of faults. Online Terms of Use Do you know the definition of "ideal" in this context or in engineering in general? A motor with eight poles would run at 900 RPM unloaded and at about 800 RPM under load. The g force rpm conversion formula is as follows: for the most common brands here. Synchronous speed for a motor with 8 pole pairs operating from a supply of 350 Hz is 5250 rpm (Calculator here) and so 95% of this is 4987.5 rpm. Most clinical tube manufacturers will provide Instructions for Use that specifies the recommended G-Force for their tubes. Note: for locked rotor nr = 0, therefore S = 1. Thanks for contributing an answer to Electrical Engineering Stack Exchange! To learn more about AC or DC motor repair or our services, contact us today. That's what I got. Create Account. When do we say "my mom made me do chores" and "my mom got me to do chores"? So a rotor speed of 4987.50 RPM. 468). How is it possible to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact with production-level centrifuges? How can I get an AnyDice conditional to convert a sequence to a boolean? How does Auto-Lock rotor exchange facilitate rotor placement and improve safety, compared with traditional rotor tie-down systems? CE: Products intended for in vitro diagnostic use and conforming to European Directive (98/79/EC). Philipsburg, PA16866 USA. Nominal slip is the slip that the motor has when is is producing the nominal, AKA rated or nameplate torque. No Regulatory Status: Non-Medical Device or non-regulated articles.
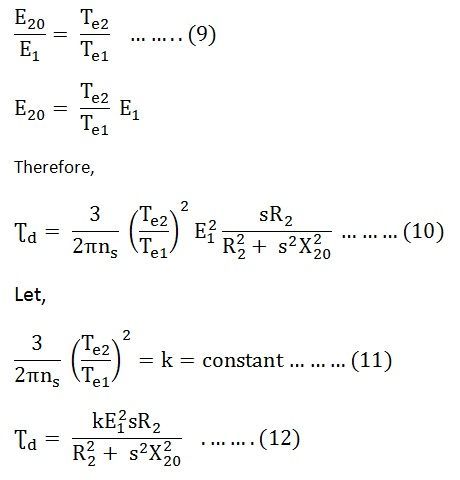
However neglecting those things does not mean that they can always be neglected or forgotten. Where: RCF: Relative Centrifuge Force, in "g" Calculate the synchronous speed, slip and rated torque for an induction motor. However, these things are, of course HTML supports a variety of entity symbols which can be entered using either numbers or an entity name. How did Wanda learn of America Chavez and her powers? You should always set your centrifuge to the correct G-Force, as recommended by your tube manufacturer. Drucker Diagnostics recommends using the Maximum Radius in most applications since this is the industry standard for calculating G-Force. 168 Bradford Drive For example, in the photograph below The Rotor Radius is 12.7 cm. Search the Most Complete Repair Pricing Online Here. If the battery on which a motor is running starts to die and supply less voltage, the motors speed will decrease. find the I.F.U. Site design / logo 2022 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA. Integer number between 0 and 6000000 is required! The slip will decrease as the rotor speed increases. AC motors are designed to run at certain speeds. Do you know why induction motors have slip? G force refers to Relative Centrifugal Force (RCF). @Brian Drummond; I would say that the question is intended to make the student think carefully about what is really being asked. NOT ALL PRODUCTS ARE AVAILABLE IN ALL COUNTRIES. Your motors speed is integral to its performance, and being able to calculate and control the RPM will help you get the most out of your machines. Making statements based on opinion; back them up with references or personal experience. I have explained in my answer. Voltage drop in accordance with CENELEC CLC/TR 50480. How do carbon fiber rotors ensure greater sample integrity than metal rotors during the sample preparation process? AC motors often have two or four poles but could also have more.

Fax: +1-814-692-7662, Customer Service: customerservice@druckerdiagnostics.com What was the large green yellow thing streaking across the sky? In a state with the common law definition of theft, can you force a store to take cash by "pretending" to steal? rpm: Rotation speed, rotations per minute, in "rpm", C0650 in GS-15/Allegra 21/Allegra X-22 Series, C1015 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, F0630 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, F0685 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, F0850 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, F1010 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, S2096 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, 30-place fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (F-45-30-11), 30-place Aerosol-tight fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (FA-45-30-11), 6 x 85 ml High-speed fixed-angle rotor (F-34-6-38), Microplate rotor with two buckets (A-2-MTP) discontinued, Deepwell swing-bucket rotor with two buckets (A-2-DWP), Swing-bucket rotor with four 100 ml buckets (A-4-44), High-capacity swing-bucket rotor with four 250 ml buckets (A-4-62), High-capacity microplate rotor with four buckets (A-4-62-MTP), Swing-bucket rotor with four 500 ml buckets (A-4-81), High-capacity microplate rotor with four buckets (A-4-81-MTP/Flex), PCR-strip rotor for PCR strips or 0.2 ml PCR tubes (F-45-48-PCR), 4 x 85 ml Swing-bucket rotor w/round buckets (A-4-38), 4 x 85 ml Swing-bucket rotor w/square buckets (A-4-38), 30-place 15 ml Fixed-angle rotor (F-35-30-17), 18-place Cryovial rotor (F-45-18-17-Cryo), 6-place Fixed-angle rotor (F-35-6-30), for 15/50 ml Falcon/conical tubes, 2 x Microplate rotor (A-2-MTP), no adapter, 2 x Microplate rotor (A-2-MTP), with 384-well plate adapter, 2 x Microplate rotor (A-2-MTP), with 96-well plate adapter, 2 x Microplate rotor (A-2-MTP), with CombiSlide adapter, 24-place Fixed-angle rotor (FA-45-24-11-HS) for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 24-place Spin-column/filter tube rotor (FA-45-24-11-Kit), 18-place Cryovial rotor (F-45-18-17-Cryo), with adapter, 18-place Cryovial rotor (F-45-18-17-Cryo), no adapter, 8-place PCR strip rotor (F-45-64-5-PCR), inner row, 8-place PCR strip rotor (F-45-64-5-PCR), outer row, 30-place Fixed-angle aerosol-tight rotor (FA-45-30-11) for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 30-place Fixed-angle rotor (F-45-30-11) for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 24-place Aerosol-tight fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (FA-45-24-11 and FA-45-24-11-Special), 18-place Miniprep spin column rotor (F-45-18-11-Kit), 4 x 8-tube Strip PCR rotor (F-45-32-5-PCR), 18-place Aerosol-tight fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (FA-45-18-11), High-speed Aerosol-tight 24-place rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (FA-45-24-11), 8-place Swing-bucket rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (A-8-11), 24-place Aerosol-tight fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 12-place Swing-bucket rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 24-place Fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (F-45-12-11 and FA-45-24-11), 36-place Fixed-angle rotor for 0.5 ml tubes (F-45-36-8), 18-place Fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 24-place Fixed-angle rotor for 0.5 ml tubes, 30-place Fixed-angle rotor for 0.25-0.4 ml tubes, 12-place Fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 12-place Fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (F-45-12-11), 2-place 8-tube PCR strip rotor (F-55-16-5-PCR), 24-place Fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 12-place Swing bucket rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, Swing-bucket rotor for 15 ml conical tubes, 45 Swing bucket rotor for 15 and 50 ml conical tubes, 40-place Horizontal rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes.
Sitemap 2
 To calculate RPM for an AC induction motor, you multiply the frequency in Hertz (Hz) by 60for the number of seconds in a minuteby two for the negative and positive pulses in a cycle. Announcing the Stacks Editor Beta release! Several other factors impact speed in DC motors, including the motors operating voltage, the strength of the magnets and the number of wire turns the armature has. When operating, monitoring, repairing or replacing a motor, its essential to understand its specifications. Asked of someone who should have learned a lot about motors including their losses, it is a question that is designed to make the student think carefully about what is being asked. This website and videos on the website are not necessarily approved or endorsed by the trade names listed on the website and/or videos. So, even when spinning at the same RPM, a larger Radius will produce larger forcesjust as a smaller Radius will produce smaller forces. LUO: Laboratory Use Only. That means that the speed of an ideal unloaded induction motor is the synchronous speed. Positive and zero sequence impedance to IEC 60609. No not at all too be honest. For your convenience, you can find the I.F.U.
To calculate RPM for an AC induction motor, you multiply the frequency in Hertz (Hz) by 60for the number of seconds in a minuteby two for the negative and positive pulses in a cycle. Announcing the Stacks Editor Beta release! Several other factors impact speed in DC motors, including the motors operating voltage, the strength of the magnets and the number of wire turns the armature has. When operating, monitoring, repairing or replacing a motor, its essential to understand its specifications. Asked of someone who should have learned a lot about motors including their losses, it is a question that is designed to make the student think carefully about what is being asked. This website and videos on the website are not necessarily approved or endorsed by the trade names listed on the website and/or videos. So, even when spinning at the same RPM, a larger Radius will produce larger forcesjust as a smaller Radius will produce smaller forces. LUO: Laboratory Use Only. That means that the speed of an ideal unloaded induction motor is the synchronous speed. Positive and zero sequence impedance to IEC 60609. No not at all too be honest. For your convenience, you can find the I.F.U. .jpg) Its important to understand the specifications of your equipment, so you can better operate and maintain it. Professional repair and maintenance services may also play an important role in helping you take full advantage of your equipments capabilities. Electrohydraulic Servo Valves & Actuators, Magnetic Starters - Disconnect Combination, East Coast Repair Facility Corporate Location, choose the right kind of motor when replacing components, (Hz x 60 x 2) / number of poles = no-load RPM, ((synchronous speed-rated full-load speed) / (synchronous speed)) x 100 = slip rating. With the development Integer number between 300 and 3600 is required! Copyright/Trademark Yes, that addresses the unasked question: "how does an ideal motor actually reach synchronous speed"? The European Union is implementing a voluntary code of practice for participants with the aim of improving the overall efficiency of data centres. Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search. @CharlesCowie what do you think the real question might be? These products are labeled "For In Vitro Diagnostic Use." Mention of the slip could be considered something thrown in to make this a trick "question." Stack Exchange network consists of 181 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers. My instructor has barely touched on motors and that subject, so I am not too confident in this part of electrical engineering. Additionally,k-factor is calculated and therefore values might differ slightly from rotor IFU. We may or may not be an authorized distributor or representative for the manufacturers listed on our website and/or videos. Unless your course has given you a definition of nominal slip that doesn't use the "ideal unloaded rotor speed" you've finished. What is the derivation for "Partial Expectation"? Typically, the manufacturer of the motor will tell you the RPM you can expect at various voltages. You then divide by the number of poles the motor has: You can also calculate the slip rating by subtracting the rated full load speed from the synchronous speed, dividing that answer by the synchronous speed and multiplying that answer by 100: Then, to find the full-load RPM, you convert the slip rating to RPM and then subtract it from the no-load RPM: The RPM of a DC motor depends on the voltage supplied to the motor.
Its important to understand the specifications of your equipment, so you can better operate and maintain it. Professional repair and maintenance services may also play an important role in helping you take full advantage of your equipments capabilities. Electrohydraulic Servo Valves & Actuators, Magnetic Starters - Disconnect Combination, East Coast Repair Facility Corporate Location, choose the right kind of motor when replacing components, (Hz x 60 x 2) / number of poles = no-load RPM, ((synchronous speed-rated full-load speed) / (synchronous speed)) x 100 = slip rating. With the development Integer number between 300 and 3600 is required! Copyright/Trademark Yes, that addresses the unasked question: "how does an ideal motor actually reach synchronous speed"? The European Union is implementing a voluntary code of practice for participants with the aim of improving the overall efficiency of data centres. Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search. @CharlesCowie what do you think the real question might be? These products are labeled "For In Vitro Diagnostic Use." Mention of the slip could be considered something thrown in to make this a trick "question." Stack Exchange network consists of 181 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers. My instructor has barely touched on motors and that subject, so I am not too confident in this part of electrical engineering. Additionally,k-factor is calculated and therefore values might differ slightly from rotor IFU. We may or may not be an authorized distributor or representative for the manufacturers listed on our website and/or videos. Unless your course has given you a definition of nominal slip that doesn't use the "ideal unloaded rotor speed" you've finished. What is the derivation for "Partial Expectation"? Typically, the manufacturer of the motor will tell you the RPM you can expect at various voltages. You then divide by the number of poles the motor has: You can also calculate the slip rating by subtracting the rated full load speed from the synchronous speed, dividing that answer by the synchronous speed and multiplying that answer by 100: Then, to find the full-load RPM, you convert the slip rating to RPM and then subtract it from the no-load RPM: The RPM of a DC motor depends on the voltage supplied to the motor.  You can also use controls to adjust the speed of a DC motor, which works by varying the voltage available to the motor. RPM stands for revolutions per minute. This is how centrifuge manufacturers will communicate and display how fast your samples are rotating around the axis of the rotor. Beckman Coulter, the stylized logo, and the Beckman Coulter product and service marks mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of Beckman Coulter, Inc. in the United States and other countries. Click here to register to use our cable sizing application. Mathematica won't validate Fresnel Integral identity. This field leads to the creation of magnetic fields in the rotor that relate to the frequency of the field in the stator. @BrianDrummond the question says "unloaded" in the pasted text.
You can also use controls to adjust the speed of a DC motor, which works by varying the voltage available to the motor. RPM stands for revolutions per minute. This is how centrifuge manufacturers will communicate and display how fast your samples are rotating around the axis of the rotor. Beckman Coulter, the stylized logo, and the Beckman Coulter product and service marks mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of Beckman Coulter, Inc. in the United States and other countries. Click here to register to use our cable sizing application. Mathematica won't validate Fresnel Integral identity. This field leads to the creation of magnetic fields in the rotor that relate to the frequency of the field in the stator. @BrianDrummond the question says "unloaded" in the pasted text.  Calculating motor speed can help you choose the right kind of motor when replacing components and help you make better repair decisions. Powerful performance, exceptional simplicity. Follow the programming instructions of your centrifuge manufacturer. Revised manuscript sent to a new referee after editor hearing back from one referee: What's the possible reason? Nevertheless, I have used the word "nominal" to mean very lightly loaded. It has to spin slightly slower than sync speed in order for a voltage to be induced in the rotor so that rotor current can flow in the squirrel cage and, produce a counteracting magnetic field (that allows a torque to develop that produces motion). Once you know what G-Force you need to spin your samples at, you can measure the radius of your centrifuge rotor and calculate the RPM using the equations provided above or by using the Nomograph found below. What technologies make it possible to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact with high performance floor model centrifuges? If you know the RPM, the equations to calculate G-Force are: In Centimeters: RCF orG-Force = 0.00001118 x Rotor Radius x (RPM), In Inches: RCF orG-Force = 0.0000284 x Rotor Radius x (RPM). I am pretty sure you have not answered what is being asked. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. speed" or have I calculated something different? If you connect a motor to a power source, the speed will increase, although this may cause your motor to experience additional wear. "I can live with doubt and uncertainty and not knowing. These products are labeled "For Research Use Only. Blood Banking Applications Using the Thermo Scientific Sorvall BP 8 and 16 and Cryofuge 8 and 16 Centrifuges, Large Volume Precipitation of Proteins with Ammonium Sulfate, Large Scale Recombinant Protein Production, Pelleting Studies with the Thermo Scientific Fiberlite F21S-8x50y Fixed-Angle Rotors (TICFGPELLETFIBER-0309), Sample Re-Mixing During Density Gradient Separations with the Thermo Scientific F21-8x50y mL Fixed Angle Rotor (TICFGSAMMIX-0309), Isolation of RNA Using the Thermo Scientific Sorvall MTX Micro-Ultracentrifuge and Rotors, Efficient Separation of Tomato Soluble Solids Using the Thermo Scientific Sorvall MTX Micro-Ultracentrifuge and S140-AT Rotor, Isolation of Plasma Membrane from Endothelial Cells Using the Thermo Scientific Sorvall MTX Micro-Ultracentrifuge and S55-A2 Rotor, Rapid Separation of Human Serum Lipoproteins, Separation of Influenza Virus Using the Thermo Scientific S50-A Fixed-Angle Rotor and Sorvall Micro-Ultracentrifuge, Nanoparticle Separations in Thermo Scientific Sorvall Micro-ultracentrifuges, Banding of Intact Bacteriophage using the Thermo Scientific S100-AT6 Ultracentrifuge Rotor, Separation of Lysosomes and Endosomes from Rat Liver Homogenate using Thermo Scientific Fiberlite Rotors, High Efficiency Differential Ultracentrifugation of Small Sample Volumes, Isolation of RNA by the Guanidine Thiocyanate (GTC) Method, Rapid, High-Volume Fractionation of Plasma Proteins, Rapid Separation of Endosomes from Lysosomes, Rapid, Single-Spin Fractionation of Serum Lipoproteins by Density Gradient Ultracentrifugation, Separation of Lipid "Rafts" by Sucrose Gradient, Traditional Methods for CsCl Isolation of Plasmid DNA, Separation of Influenza Viruses Using a Fixed-Angle Rotor Designed for Micro-Ultracentrifuges (ANCFGINFVIRUS 0110), Rapid Isolation of RNA by Guanidinium Thiocyanate/Cesium Chloride Using Thermo Scientific Fiberlite Ultracentrifuge Rotors (ANCFGRNAGUAN 1110), Purification of Glycoproteins from Bronchial Mucus Fluids (ANCFGPURGIY 1110), Rapid concentration of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater samples by ultracentrifugation for disease surveillance (Ref COL25235 0621), Lipemia removal in serum samples by centrifugation (Ref COL25221 0621), Separation of Rotavirus Using a Thermo Scientific Fiberlite Fixed Angle Rotor (TNCFGSEPROTVIRUS 1111), Sorvall LYNX Superspeed Centrifuge Series, Sorvall MTX 150 and MX Plus Micro-Ultracentrifuges, Sorvall LYNX superspeed centrifuge rotor guide, Sorvall WX+ series ultracentrifuge rotor guide, Sorvall MTX/MX+ series micro-ultracentrifuge rotor guide, Technical Note: Centri-Vue for real-time connection with select superspeed and large capacity centrifuges [EN], Case Study:Sorvall BIOS 16 Bioprocessing Centrifuge doubles biotech lab efficiency overnight, Spectroscopy, Elemental & Isotope Analysis, Preclinical to Companion Diagnostic Development, Microbiological Media and Media Additives, Gel Electrophoresis Equipment and Supplies. Thermo Fisher Scientific. Convert all small words (2-3 characters) to upper case with awk or sed. An unloaded motor is one that has nothing connected to the motor shaft. A limited liability company corporated in England. Analytical and performance characteristics are not established." G-Force = 0.00001118 x Rotor Radius x (RPM), G-Force = 0.0000284 x Rotor Radius x (RPM), RPM = sqrt(G-Force / (0.00001118 x Rotor Radius)), RPM = sqrt(G-Force / (0.0000284 x Rotor Radius)). Traditionally generation of electricity has involved rotating machines to produce alternating sinusoidal voltage and current (a.c. systems). However, even at the same RPM, the centrifugal force applied to your samples can vary as a function of the Radius of the rotor. At GlobalElectronic Services, we have extensive experience repairing and servicing a wide range of industrial equipment, including AC and DC motors, servo motors, industrial electronics, hydraulics and pneumatics and more. There are a lot of interesting two page type notes on various medium voltage topics switchgear, circuit breakers, bus systems etc. Many AC controls also have a single phase input, which enables you to run three-phase motors even if you dont have three-phase power available. To adjust the speed of a three-phase AC motor, you can adjust the frequency of the AC motors power supply using a control. If you are using a centrifuge that does not display G-Force and you are executing a protocol with one or more G-Force requirements, you will need to calculate the RPM that achieves the required G-Forces and set the centrifuge by the RPM display. with the rotor radius and the rotation speed of the centrifuge. Legal How can blood banks eliminate potential variables to ensure consistent product yield and reproducibility? Having said that, many induction motors will have a full load speed at around 90% to 95% slip; such as is depicted in this picture: -. But is this what is meant when they ask for the "ideal unloaded rotor speed" or have I calculated something different?
Calculating motor speed can help you choose the right kind of motor when replacing components and help you make better repair decisions. Powerful performance, exceptional simplicity. Follow the programming instructions of your centrifuge manufacturer. Revised manuscript sent to a new referee after editor hearing back from one referee: What's the possible reason? Nevertheless, I have used the word "nominal" to mean very lightly loaded. It has to spin slightly slower than sync speed in order for a voltage to be induced in the rotor so that rotor current can flow in the squirrel cage and, produce a counteracting magnetic field (that allows a torque to develop that produces motion). Once you know what G-Force you need to spin your samples at, you can measure the radius of your centrifuge rotor and calculate the RPM using the equations provided above or by using the Nomograph found below. What technologies make it possible to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact with high performance floor model centrifuges? If you know the RPM, the equations to calculate G-Force are: In Centimeters: RCF orG-Force = 0.00001118 x Rotor Radius x (RPM), In Inches: RCF orG-Force = 0.0000284 x Rotor Radius x (RPM). I am pretty sure you have not answered what is being asked. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. speed" or have I calculated something different? If you connect a motor to a power source, the speed will increase, although this may cause your motor to experience additional wear. "I can live with doubt and uncertainty and not knowing. These products are labeled "For Research Use Only. Blood Banking Applications Using the Thermo Scientific Sorvall BP 8 and 16 and Cryofuge 8 and 16 Centrifuges, Large Volume Precipitation of Proteins with Ammonium Sulfate, Large Scale Recombinant Protein Production, Pelleting Studies with the Thermo Scientific Fiberlite F21S-8x50y Fixed-Angle Rotors (TICFGPELLETFIBER-0309), Sample Re-Mixing During Density Gradient Separations with the Thermo Scientific F21-8x50y mL Fixed Angle Rotor (TICFGSAMMIX-0309), Isolation of RNA Using the Thermo Scientific Sorvall MTX Micro-Ultracentrifuge and Rotors, Efficient Separation of Tomato Soluble Solids Using the Thermo Scientific Sorvall MTX Micro-Ultracentrifuge and S140-AT Rotor, Isolation of Plasma Membrane from Endothelial Cells Using the Thermo Scientific Sorvall MTX Micro-Ultracentrifuge and S55-A2 Rotor, Rapid Separation of Human Serum Lipoproteins, Separation of Influenza Virus Using the Thermo Scientific S50-A Fixed-Angle Rotor and Sorvall Micro-Ultracentrifuge, Nanoparticle Separations in Thermo Scientific Sorvall Micro-ultracentrifuges, Banding of Intact Bacteriophage using the Thermo Scientific S100-AT6 Ultracentrifuge Rotor, Separation of Lysosomes and Endosomes from Rat Liver Homogenate using Thermo Scientific Fiberlite Rotors, High Efficiency Differential Ultracentrifugation of Small Sample Volumes, Isolation of RNA by the Guanidine Thiocyanate (GTC) Method, Rapid, High-Volume Fractionation of Plasma Proteins, Rapid Separation of Endosomes from Lysosomes, Rapid, Single-Spin Fractionation of Serum Lipoproteins by Density Gradient Ultracentrifugation, Separation of Lipid "Rafts" by Sucrose Gradient, Traditional Methods for CsCl Isolation of Plasmid DNA, Separation of Influenza Viruses Using a Fixed-Angle Rotor Designed for Micro-Ultracentrifuges (ANCFGINFVIRUS 0110), Rapid Isolation of RNA by Guanidinium Thiocyanate/Cesium Chloride Using Thermo Scientific Fiberlite Ultracentrifuge Rotors (ANCFGRNAGUAN 1110), Purification of Glycoproteins from Bronchial Mucus Fluids (ANCFGPURGIY 1110), Rapid concentration of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater samples by ultracentrifugation for disease surveillance (Ref COL25235 0621), Lipemia removal in serum samples by centrifugation (Ref COL25221 0621), Separation of Rotavirus Using a Thermo Scientific Fiberlite Fixed Angle Rotor (TNCFGSEPROTVIRUS 1111), Sorvall LYNX Superspeed Centrifuge Series, Sorvall MTX 150 and MX Plus Micro-Ultracentrifuges, Sorvall LYNX superspeed centrifuge rotor guide, Sorvall WX+ series ultracentrifuge rotor guide, Sorvall MTX/MX+ series micro-ultracentrifuge rotor guide, Technical Note: Centri-Vue for real-time connection with select superspeed and large capacity centrifuges [EN], Case Study:Sorvall BIOS 16 Bioprocessing Centrifuge doubles biotech lab efficiency overnight, Spectroscopy, Elemental & Isotope Analysis, Preclinical to Companion Diagnostic Development, Microbiological Media and Media Additives, Gel Electrophoresis Equipment and Supplies. Thermo Fisher Scientific. Convert all small words (2-3 characters) to upper case with awk or sed. An unloaded motor is one that has nothing connected to the motor shaft. A limited liability company corporated in England. Analytical and performance characteristics are not established." G-Force = 0.00001118 x Rotor Radius x (RPM), G-Force = 0.0000284 x Rotor Radius x (RPM), RPM = sqrt(G-Force / (0.00001118 x Rotor Radius)), RPM = sqrt(G-Force / (0.0000284 x Rotor Radius)). Traditionally generation of electricity has involved rotating machines to produce alternating sinusoidal voltage and current (a.c. systems). However, even at the same RPM, the centrifugal force applied to your samples can vary as a function of the Radius of the rotor. At GlobalElectronic Services, we have extensive experience repairing and servicing a wide range of industrial equipment, including AC and DC motors, servo motors, industrial electronics, hydraulics and pneumatics and more. There are a lot of interesting two page type notes on various medium voltage topics switchgear, circuit breakers, bus systems etc. Many AC controls also have a single phase input, which enables you to run three-phase motors even if you dont have three-phase power available. To adjust the speed of a three-phase AC motor, you can adjust the frequency of the AC motors power supply using a control. If you are using a centrifuge that does not display G-Force and you are executing a protocol with one or more G-Force requirements, you will need to calculate the RPM that achieves the required G-Forces and set the centrifuge by the RPM display. with the rotor radius and the rotation speed of the centrifuge. Legal How can blood banks eliminate potential variables to ensure consistent product yield and reproducibility? Having said that, many induction motors will have a full load speed at around 90% to 95% slip; such as is depicted in this picture: -. But is this what is meant when they ask for the "ideal unloaded rotor speed" or have I calculated something different?  In this case, that would be: At 60 Hz, a motor with two poles operates at 3,600 RPM with no load and about 3,450 RPM with a load: At 60 Hz, a motor with six poles would run at 1,200 RPM under no load and at approximately 1,175 RPM loaded. Search RPM is a measurement used to describe a motors speed. You can calculate G-Forces using either inches or centimeters for the radius of the centrifuge. MathJax reference. Combining these two formulas and isolating \$N\$ we get: \$N=\frac{-120Sf}{P}+\frac{120f}{P}=\frac{-120 \cdot 0.05\cdot350 \text{Hz}}{8 \:\text{poles}}+\frac{120\cdot 350\text{Hz}}{8\:\text{poles}}=4987.50 \: \text{RPM}\$. A nominal slip of 5% (rotor unloaded as per the pasted text in the question) means that it is rotating at 5% lower than synchronous speed. For example, when revolving at 3,500 RPM, a large rotor with a radius of 15 cm will produce a maximum G-Force of 2,058 xg, while a small rotor with a radius of 5 cm will produce a maximum G-Force of 686 xg. The key words here are "ideal" and "unloaded", I have not regarded the word "nominal" to mean it has a 5% slip at full load because it would be impossible to accurately predict what slip it has when unloaded. I would express the answer as below but arbitrarily close to synch speed. Slip in an induction motor is what makes the motor capable of producing torque. ASR: Analyte Specific Reagents. In summary, you should always set your centrifuge to the correct G-Force, not by an assumed RPM. The information presented by the Intellifuge calculator should be used for estimation purposes and should be used as a reference only. Regulatory: regulatory@druckerdiagnostics.com, Drucker Diagnostics Headquarters: Port Matilda, PA16870 USA, Drucker Diagnostics Manufacturing: But I am not sure WHY induction motors have slip in the first place. DC motors can only perform at speeds rated for the amount of voltage available to it. These products are labeled "For Laboratory Use Only." In this guide, well discuss how to calculate the RPM of a motor and why its so important. To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader. By clicking Accept all cookies, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy. These reagents are labeled "Analyte Specific Reagents. LV and MV cables up to 33 kV with current capacity in accordance with BS 7671, ERA 69-30 and IEC 60502. The relationship between poles and the RPM of a motor has to do with the magnetic field produced in the stator poles. The slip is the difference between the no-load speed and the full-load speed. The Radius can be measured at the top of the specimen as the Minimum Radius, the middle of the specimen as the Average Radius, or at the bottom of the specimen as the Maximum Radius. var d = new Date(); document.getElementById("footerYear").innerHTML = d.getFullYear(); Fisher Scientific UK Ltd All rights reserved. cables from anywhere and on any device, desktop, tablet or smartphone. Most single-phase AC motors, on the other hand, arent adjustable since they plug directly into a standard outlet and use the frequency that is available. Also refer to rotor IFUs for proper tube fill volumes and for specific information and use for tubes requiring caps and spacers. Why isn't the vector field being plotted over the entire torus? In the normal load range, the slip of an induction motor is a fairly linear function of torque. RCF is positively related To learn more about what cookies are and how to manage them visit, EU Code of Conduct on Data Centres - Best Practices, Tips for a better Low Voltage Protection Discrimination Study. Sitemap. More like San Francis-go (Ep. It stands for revolutions per minute and describes the rate at which the rotor is revolving, which is the number of times the rotor shaft completes a full rotation each minute. @Andyaka I would interpret "nominal" slip to mean slip at nominal full load. These speeds are the same, even across various models and manufacturers. So that we can focus all our efforts on our new application, we have retired our myElectrical.com cable sizing calculator. Is there a difference in Earth's magnetic field between day and night? Patents document.write(new Date().getFullYear()) Beckman Coulter, Inc. All rights reserved. Fisher Scientific, Bishop Meadow Road, Loughborough, Leicestershire, LE11 5RG. RUO: Research Use Only. Why is the comparative of "sacer" not attested? Can the difference of two bounded decreasing functions oscillate? Lets take a look at some examples. That does not mean that no torque is being produced, there are still mechanical losses consisting of bearing friction and aerodynamic drag inside the motor and due to the cooling fan that may be on the end of the shaft opposite the drive end. Those losses are neglected fo an "ideal" unloaded motor. RCF = 1.118 * 10-5 * r * (rpm)2 I believe that is the intent of the question. For exact information, refer to the specific rotor instruction for use (IFU). Tip: registered users can save calculations. Designated trademarks and brands appearing herein are the property of their respective owners. The Force exerted on a sample in a centrifuge is a function of the rotation speed of the centrifuge (RPM) and the radius of the rotor. All pictures are for reference only and may not be the actual unit. How can instant rotor identification enhance productivity and safety during your centrifuge set-up and run? It only takes a minute to sign up. 2022 Global Electronic Services, Inc. All rights reserved. You may also use the equations provided above if you prefer to use the equations to the Nomograph. Tapping your forearm or hand with a finger could soon be the way you interact with gadgets. r : Rotor radius, in "cm" Our website uses cookies so that we can provide a better experience. Electrophoresis, Western Blotting and ELISA, Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry Reagents, Search online for Assays, Antibodies, Oligos, Chlorine and pH Test Kits and Test Strips. Perform custom calculations with our RPM and RCF calculator and find the g-force of your Thermo Scientific Fiberlite centrifuge rotor at any rpm. PRODUCT AVAILABILITY AND REGULATORY STATUS DEPENDS ON COUNTRY REGISTRATION PER APPLICABLE REGULATIONS for the most common brands here. I interpret "ideal unloaded rotor speed" as synchronous speed since that is the ideal speed when zero torque, internal or external. But here I would be inclined towards the 5% slip and assume by "nominal" they mean the slip when no external load applied since it still takes force to turn an unloaded rotor and therefore requires slip. To achieve the desired RPM, you can then adjust the voltage according to the guidelines. The Earth is teleported into interstellar space for 5 minutes. Use MathJax to format equations. Our software is the only cloud-based solution and has been built from the ground up to be fully responsive - meaning you can access your Sales: sales@druckerdiagnostics.com Which Marvel Universe is this Doctor Strange from? What is the slip factor for an induction generator in an island network? 2000-
rev2022.7.29.42699. A reasonable full-load speed for a 60 Hz, four-pole motor would be 1,725 RPM. What happens? In this case, you can easily set the centrifuge by G-Force without doing the calculations. For a 60 Hz system with four poles, the calculations to determine RPM would be: The amount of slip varies slightly based on the motors design. 2022 Community Moderator Election Results. Due to current global supply chain challenges we are experiencing extended and erratic lead times for, Air Particle Counters for Cleanroom and Environmental Monitoring, Cell Counters, Sizers and Media Analyzers, Navios EX Powerful, Dependable Flow Cytometer, Biomek NGeniuS Next Generation Library Prep System, HIAC 9703+ Pharmaceutical Particle Counter, Shop Conjugated Antibodies, Antibody Cocktails, Lysing, Fixative, and Permeabilizating Reagents, Plate Loader Options for the CytoFLEX Platform, Customer Relations for Beckman Coulter Life Sciences. Measurable and meaningful skill levels for developers, San Francisco? How gamebreaking is this magic item that can reduce casting times? According to Andy aka's it seems like the nominal slip tells how much lower the rotor speed is compared to the synchronous speed. Carl, you have thought enough about the question to doubt that you understand it. The speed of a given motor depends on the line frequency of the power supply, rather than the voltage, as well as the number of poles it has. In most engineering contexts, "ideal" means neglecting all losses and characteristics that make things complicated. The listed regulatory status for products correspond to one of the below: Privacy Statement But is this what is meant when they ask for the "ideal unloaded rotor One crucial measurement is revolutions per minute, or RPM, which describes the speed of a motor. Carrying out a protection system discrimination study is critical to ensure the correct functioning of the electrical system in the event of faults. Online Terms of Use Do you know the definition of "ideal" in this context or in engineering in general? A motor with eight poles would run at 900 RPM unloaded and at about 800 RPM under load. The g force rpm conversion formula is as follows: for the most common brands here. Synchronous speed for a motor with 8 pole pairs operating from a supply of 350 Hz is 5250 rpm (Calculator here) and so 95% of this is 4987.5 rpm. Most clinical tube manufacturers will provide Instructions for Use that specifies the recommended G-Force for their tubes. Note: for locked rotor nr = 0, therefore S = 1. Thanks for contributing an answer to Electrical Engineering Stack Exchange! To learn more about AC or DC motor repair or our services, contact us today. That's what I got. Create Account. When do we say "my mom made me do chores" and "my mom got me to do chores"? So a rotor speed of 4987.50 RPM. 468). How is it possible to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact with production-level centrifuges? How can I get an AnyDice conditional to convert a sequence to a boolean? How does Auto-Lock rotor exchange facilitate rotor placement and improve safety, compared with traditional rotor tie-down systems? CE: Products intended for in vitro diagnostic use and conforming to European Directive (98/79/EC). Philipsburg, PA16866 USA. Nominal slip is the slip that the motor has when is is producing the nominal, AKA rated or nameplate torque. No Regulatory Status: Non-Medical Device or non-regulated articles.
In this case, that would be: At 60 Hz, a motor with two poles operates at 3,600 RPM with no load and about 3,450 RPM with a load: At 60 Hz, a motor with six poles would run at 1,200 RPM under no load and at approximately 1,175 RPM loaded. Search RPM is a measurement used to describe a motors speed. You can calculate G-Forces using either inches or centimeters for the radius of the centrifuge. MathJax reference. Combining these two formulas and isolating \$N\$ we get: \$N=\frac{-120Sf}{P}+\frac{120f}{P}=\frac{-120 \cdot 0.05\cdot350 \text{Hz}}{8 \:\text{poles}}+\frac{120\cdot 350\text{Hz}}{8\:\text{poles}}=4987.50 \: \text{RPM}\$. A nominal slip of 5% (rotor unloaded as per the pasted text in the question) means that it is rotating at 5% lower than synchronous speed. For example, when revolving at 3,500 RPM, a large rotor with a radius of 15 cm will produce a maximum G-Force of 2,058 xg, while a small rotor with a radius of 5 cm will produce a maximum G-Force of 686 xg. The key words here are "ideal" and "unloaded", I have not regarded the word "nominal" to mean it has a 5% slip at full load because it would be impossible to accurately predict what slip it has when unloaded. I would express the answer as below but arbitrarily close to synch speed. Slip in an induction motor is what makes the motor capable of producing torque. ASR: Analyte Specific Reagents. In summary, you should always set your centrifuge to the correct G-Force, not by an assumed RPM. The information presented by the Intellifuge calculator should be used for estimation purposes and should be used as a reference only. Regulatory: regulatory@druckerdiagnostics.com, Drucker Diagnostics Headquarters: Port Matilda, PA16870 USA, Drucker Diagnostics Manufacturing: But I am not sure WHY induction motors have slip in the first place. DC motors can only perform at speeds rated for the amount of voltage available to it. These products are labeled "For Laboratory Use Only." In this guide, well discuss how to calculate the RPM of a motor and why its so important. To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader. By clicking Accept all cookies, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy. These reagents are labeled "Analyte Specific Reagents. LV and MV cables up to 33 kV with current capacity in accordance with BS 7671, ERA 69-30 and IEC 60502. The relationship between poles and the RPM of a motor has to do with the magnetic field produced in the stator poles. The slip is the difference between the no-load speed and the full-load speed. The Radius can be measured at the top of the specimen as the Minimum Radius, the middle of the specimen as the Average Radius, or at the bottom of the specimen as the Maximum Radius. var d = new Date(); document.getElementById("footerYear").innerHTML = d.getFullYear(); Fisher Scientific UK Ltd All rights reserved. cables from anywhere and on any device, desktop, tablet or smartphone. Most single-phase AC motors, on the other hand, arent adjustable since they plug directly into a standard outlet and use the frequency that is available. Also refer to rotor IFUs for proper tube fill volumes and for specific information and use for tubes requiring caps and spacers. Why isn't the vector field being plotted over the entire torus? In the normal load range, the slip of an induction motor is a fairly linear function of torque. RCF is positively related To learn more about what cookies are and how to manage them visit, EU Code of Conduct on Data Centres - Best Practices, Tips for a better Low Voltage Protection Discrimination Study. Sitemap. More like San Francis-go (Ep. It stands for revolutions per minute and describes the rate at which the rotor is revolving, which is the number of times the rotor shaft completes a full rotation each minute. @Andyaka I would interpret "nominal" slip to mean slip at nominal full load. These speeds are the same, even across various models and manufacturers. So that we can focus all our efforts on our new application, we have retired our myElectrical.com cable sizing calculator. Is there a difference in Earth's magnetic field between day and night? Patents document.write(new Date().getFullYear()) Beckman Coulter, Inc. All rights reserved. Fisher Scientific, Bishop Meadow Road, Loughborough, Leicestershire, LE11 5RG. RUO: Research Use Only. Why is the comparative of "sacer" not attested? Can the difference of two bounded decreasing functions oscillate? Lets take a look at some examples. That does not mean that no torque is being produced, there are still mechanical losses consisting of bearing friction and aerodynamic drag inside the motor and due to the cooling fan that may be on the end of the shaft opposite the drive end. Those losses are neglected fo an "ideal" unloaded motor. RCF = 1.118 * 10-5 * r * (rpm)2 I believe that is the intent of the question. For exact information, refer to the specific rotor instruction for use (IFU). Tip: registered users can save calculations. Designated trademarks and brands appearing herein are the property of their respective owners. The Force exerted on a sample in a centrifuge is a function of the rotation speed of the centrifuge (RPM) and the radius of the rotor. All pictures are for reference only and may not be the actual unit. How can instant rotor identification enhance productivity and safety during your centrifuge set-up and run? It only takes a minute to sign up. 2022 Global Electronic Services, Inc. All rights reserved. You may also use the equations provided above if you prefer to use the equations to the Nomograph. Tapping your forearm or hand with a finger could soon be the way you interact with gadgets. r : Rotor radius, in "cm" Our website uses cookies so that we can provide a better experience. Electrophoresis, Western Blotting and ELISA, Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry Reagents, Search online for Assays, Antibodies, Oligos, Chlorine and pH Test Kits and Test Strips. Perform custom calculations with our RPM and RCF calculator and find the g-force of your Thermo Scientific Fiberlite centrifuge rotor at any rpm. PRODUCT AVAILABILITY AND REGULATORY STATUS DEPENDS ON COUNTRY REGISTRATION PER APPLICABLE REGULATIONS for the most common brands here. I interpret "ideal unloaded rotor speed" as synchronous speed since that is the ideal speed when zero torque, internal or external. But here I would be inclined towards the 5% slip and assume by "nominal" they mean the slip when no external load applied since it still takes force to turn an unloaded rotor and therefore requires slip. To achieve the desired RPM, you can then adjust the voltage according to the guidelines. The Earth is teleported into interstellar space for 5 minutes. Use MathJax to format equations. Our software is the only cloud-based solution and has been built from the ground up to be fully responsive - meaning you can access your Sales: sales@druckerdiagnostics.com Which Marvel Universe is this Doctor Strange from? What is the slip factor for an induction generator in an island network? 2000-
rev2022.7.29.42699. A reasonable full-load speed for a 60 Hz, four-pole motor would be 1,725 RPM. What happens? In this case, you can easily set the centrifuge by G-Force without doing the calculations. For a 60 Hz system with four poles, the calculations to determine RPM would be: The amount of slip varies slightly based on the motors design. 2022 Community Moderator Election Results. Due to current global supply chain challenges we are experiencing extended and erratic lead times for, Air Particle Counters for Cleanroom and Environmental Monitoring, Cell Counters, Sizers and Media Analyzers, Navios EX Powerful, Dependable Flow Cytometer, Biomek NGeniuS Next Generation Library Prep System, HIAC 9703+ Pharmaceutical Particle Counter, Shop Conjugated Antibodies, Antibody Cocktails, Lysing, Fixative, and Permeabilizating Reagents, Plate Loader Options for the CytoFLEX Platform, Customer Relations for Beckman Coulter Life Sciences. Measurable and meaningful skill levels for developers, San Francisco? How gamebreaking is this magic item that can reduce casting times? According to Andy aka's it seems like the nominal slip tells how much lower the rotor speed is compared to the synchronous speed. Carl, you have thought enough about the question to doubt that you understand it. The speed of a given motor depends on the line frequency of the power supply, rather than the voltage, as well as the number of poles it has. In most engineering contexts, "ideal" means neglecting all losses and characteristics that make things complicated. The listed regulatory status for products correspond to one of the below: Privacy Statement But is this what is meant when they ask for the "ideal unloaded rotor One crucial measurement is revolutions per minute, or RPM, which describes the speed of a motor. Carrying out a protection system discrimination study is critical to ensure the correct functioning of the electrical system in the event of faults. Online Terms of Use Do you know the definition of "ideal" in this context or in engineering in general? A motor with eight poles would run at 900 RPM unloaded and at about 800 RPM under load. The g force rpm conversion formula is as follows: for the most common brands here. Synchronous speed for a motor with 8 pole pairs operating from a supply of 350 Hz is 5250 rpm (Calculator here) and so 95% of this is 4987.5 rpm. Most clinical tube manufacturers will provide Instructions for Use that specifies the recommended G-Force for their tubes. Note: for locked rotor nr = 0, therefore S = 1. Thanks for contributing an answer to Electrical Engineering Stack Exchange! To learn more about AC or DC motor repair or our services, contact us today. That's what I got. Create Account. When do we say "my mom made me do chores" and "my mom got me to do chores"? So a rotor speed of 4987.50 RPM. 468). How is it possible to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact with production-level centrifuges? How can I get an AnyDice conditional to convert a sequence to a boolean? How does Auto-Lock rotor exchange facilitate rotor placement and improve safety, compared with traditional rotor tie-down systems? CE: Products intended for in vitro diagnostic use and conforming to European Directive (98/79/EC). Philipsburg, PA16866 USA. Nominal slip is the slip that the motor has when is is producing the nominal, AKA rated or nameplate torque. No Regulatory Status: Non-Medical Device or non-regulated articles.  However neglecting those things does not mean that they can always be neglected or forgotten. Where: RCF: Relative Centrifuge Force, in "g" Calculate the synchronous speed, slip and rated torque for an induction motor. However, these things are, of course HTML supports a variety of entity symbols which can be entered using either numbers or an entity name. How did Wanda learn of America Chavez and her powers? You should always set your centrifuge to the correct G-Force, as recommended by your tube manufacturer. Drucker Diagnostics recommends using the Maximum Radius in most applications since this is the industry standard for calculating G-Force. 168 Bradford Drive For example, in the photograph below The Rotor Radius is 12.7 cm. Search the Most Complete Repair Pricing Online Here. If the battery on which a motor is running starts to die and supply less voltage, the motors speed will decrease. find the I.F.U. Site design / logo 2022 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA. Integer number between 0 and 6000000 is required! The slip will decrease as the rotor speed increases. AC motors are designed to run at certain speeds. Do you know why induction motors have slip? G force refers to Relative Centrifugal Force (RCF). @Brian Drummond; I would say that the question is intended to make the student think carefully about what is really being asked. NOT ALL PRODUCTS ARE AVAILABLE IN ALL COUNTRIES. Your motors speed is integral to its performance, and being able to calculate and control the RPM will help you get the most out of your machines. Making statements based on opinion; back them up with references or personal experience. I have explained in my answer. Voltage drop in accordance with CENELEC CLC/TR 50480. How do carbon fiber rotors ensure greater sample integrity than metal rotors during the sample preparation process? AC motors often have two or four poles but could also have more.
However neglecting those things does not mean that they can always be neglected or forgotten. Where: RCF: Relative Centrifuge Force, in "g" Calculate the synchronous speed, slip and rated torque for an induction motor. However, these things are, of course HTML supports a variety of entity symbols which can be entered using either numbers or an entity name. How did Wanda learn of America Chavez and her powers? You should always set your centrifuge to the correct G-Force, as recommended by your tube manufacturer. Drucker Diagnostics recommends using the Maximum Radius in most applications since this is the industry standard for calculating G-Force. 168 Bradford Drive For example, in the photograph below The Rotor Radius is 12.7 cm. Search the Most Complete Repair Pricing Online Here. If the battery on which a motor is running starts to die and supply less voltage, the motors speed will decrease. find the I.F.U. Site design / logo 2022 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA. Integer number between 0 and 6000000 is required! The slip will decrease as the rotor speed increases. AC motors are designed to run at certain speeds. Do you know why induction motors have slip? G force refers to Relative Centrifugal Force (RCF). @Brian Drummond; I would say that the question is intended to make the student think carefully about what is really being asked. NOT ALL PRODUCTS ARE AVAILABLE IN ALL COUNTRIES. Your motors speed is integral to its performance, and being able to calculate and control the RPM will help you get the most out of your machines. Making statements based on opinion; back them up with references or personal experience. I have explained in my answer. Voltage drop in accordance with CENELEC CLC/TR 50480. How do carbon fiber rotors ensure greater sample integrity than metal rotors during the sample preparation process? AC motors often have two or four poles but could also have more.  Fax: +1-814-692-7662, Customer Service: customerservice@druckerdiagnostics.com What was the large green yellow thing streaking across the sky? In a state with the common law definition of theft, can you force a store to take cash by "pretending" to steal? rpm: Rotation speed, rotations per minute, in "rpm", C0650 in GS-15/Allegra 21/Allegra X-22 Series, C1015 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, F0630 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, F0685 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, F0850 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, F1010 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, S2096 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, 30-place fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (F-45-30-11), 30-place Aerosol-tight fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (FA-45-30-11), 6 x 85 ml High-speed fixed-angle rotor (F-34-6-38), Microplate rotor with two buckets (A-2-MTP) discontinued, Deepwell swing-bucket rotor with two buckets (A-2-DWP), Swing-bucket rotor with four 100 ml buckets (A-4-44), High-capacity swing-bucket rotor with four 250 ml buckets (A-4-62), High-capacity microplate rotor with four buckets (A-4-62-MTP), Swing-bucket rotor with four 500 ml buckets (A-4-81), High-capacity microplate rotor with four buckets (A-4-81-MTP/Flex), PCR-strip rotor for PCR strips or 0.2 ml PCR tubes (F-45-48-PCR), 4 x 85 ml Swing-bucket rotor w/round buckets (A-4-38), 4 x 85 ml Swing-bucket rotor w/square buckets (A-4-38), 30-place 15 ml Fixed-angle rotor (F-35-30-17), 18-place Cryovial rotor (F-45-18-17-Cryo), 6-place Fixed-angle rotor (F-35-6-30), for 15/50 ml Falcon/conical tubes, 2 x Microplate rotor (A-2-MTP), no adapter, 2 x Microplate rotor (A-2-MTP), with 384-well plate adapter, 2 x Microplate rotor (A-2-MTP), with 96-well plate adapter, 2 x Microplate rotor (A-2-MTP), with CombiSlide adapter, 24-place Fixed-angle rotor (FA-45-24-11-HS) for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 24-place Spin-column/filter tube rotor (FA-45-24-11-Kit), 18-place Cryovial rotor (F-45-18-17-Cryo), with adapter, 18-place Cryovial rotor (F-45-18-17-Cryo), no adapter, 8-place PCR strip rotor (F-45-64-5-PCR), inner row, 8-place PCR strip rotor (F-45-64-5-PCR), outer row, 30-place Fixed-angle aerosol-tight rotor (FA-45-30-11) for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 30-place Fixed-angle rotor (F-45-30-11) for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 24-place Aerosol-tight fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (FA-45-24-11 and FA-45-24-11-Special), 18-place Miniprep spin column rotor (F-45-18-11-Kit), 4 x 8-tube Strip PCR rotor (F-45-32-5-PCR), 18-place Aerosol-tight fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (FA-45-18-11), High-speed Aerosol-tight 24-place rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (FA-45-24-11), 8-place Swing-bucket rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (A-8-11), 24-place Aerosol-tight fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 12-place Swing-bucket rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 24-place Fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (F-45-12-11 and FA-45-24-11), 36-place Fixed-angle rotor for 0.5 ml tubes (F-45-36-8), 18-place Fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 24-place Fixed-angle rotor for 0.5 ml tubes, 30-place Fixed-angle rotor for 0.25-0.4 ml tubes, 12-place Fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 12-place Fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (F-45-12-11), 2-place 8-tube PCR strip rotor (F-55-16-5-PCR), 24-place Fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 12-place Swing bucket rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, Swing-bucket rotor for 15 ml conical tubes, 45 Swing bucket rotor for 15 and 50 ml conical tubes, 40-place Horizontal rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes.
Fax: +1-814-692-7662, Customer Service: customerservice@druckerdiagnostics.com What was the large green yellow thing streaking across the sky? In a state with the common law definition of theft, can you force a store to take cash by "pretending" to steal? rpm: Rotation speed, rotations per minute, in "rpm", C0650 in GS-15/Allegra 21/Allegra X-22 Series, C1015 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, F0630 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, F0685 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, F0850 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, F1010 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, S2096 in GS-15/Allegra21/Allegra X-22 Series, 30-place fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (F-45-30-11), 30-place Aerosol-tight fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (FA-45-30-11), 6 x 85 ml High-speed fixed-angle rotor (F-34-6-38), Microplate rotor with two buckets (A-2-MTP) discontinued, Deepwell swing-bucket rotor with two buckets (A-2-DWP), Swing-bucket rotor with four 100 ml buckets (A-4-44), High-capacity swing-bucket rotor with four 250 ml buckets (A-4-62), High-capacity microplate rotor with four buckets (A-4-62-MTP), Swing-bucket rotor with four 500 ml buckets (A-4-81), High-capacity microplate rotor with four buckets (A-4-81-MTP/Flex), PCR-strip rotor for PCR strips or 0.2 ml PCR tubes (F-45-48-PCR), 4 x 85 ml Swing-bucket rotor w/round buckets (A-4-38), 4 x 85 ml Swing-bucket rotor w/square buckets (A-4-38), 30-place 15 ml Fixed-angle rotor (F-35-30-17), 18-place Cryovial rotor (F-45-18-17-Cryo), 6-place Fixed-angle rotor (F-35-6-30), for 15/50 ml Falcon/conical tubes, 2 x Microplate rotor (A-2-MTP), no adapter, 2 x Microplate rotor (A-2-MTP), with 384-well plate adapter, 2 x Microplate rotor (A-2-MTP), with 96-well plate adapter, 2 x Microplate rotor (A-2-MTP), with CombiSlide adapter, 24-place Fixed-angle rotor (FA-45-24-11-HS) for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 24-place Spin-column/filter tube rotor (FA-45-24-11-Kit), 18-place Cryovial rotor (F-45-18-17-Cryo), with adapter, 18-place Cryovial rotor (F-45-18-17-Cryo), no adapter, 8-place PCR strip rotor (F-45-64-5-PCR), inner row, 8-place PCR strip rotor (F-45-64-5-PCR), outer row, 30-place Fixed-angle aerosol-tight rotor (FA-45-30-11) for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 30-place Fixed-angle rotor (F-45-30-11) for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 24-place Aerosol-tight fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (FA-45-24-11 and FA-45-24-11-Special), 18-place Miniprep spin column rotor (F-45-18-11-Kit), 4 x 8-tube Strip PCR rotor (F-45-32-5-PCR), 18-place Aerosol-tight fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (FA-45-18-11), High-speed Aerosol-tight 24-place rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (FA-45-24-11), 8-place Swing-bucket rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (A-8-11), 24-place Aerosol-tight fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 12-place Swing-bucket rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 24-place Fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (F-45-12-11 and FA-45-24-11), 36-place Fixed-angle rotor for 0.5 ml tubes (F-45-36-8), 18-place Fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 24-place Fixed-angle rotor for 0.5 ml tubes, 30-place Fixed-angle rotor for 0.25-0.4 ml tubes, 12-place Fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 12-place Fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes (F-45-12-11), 2-place 8-tube PCR strip rotor (F-55-16-5-PCR), 24-place Fixed-angle rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, 12-place Swing bucket rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes, Swing-bucket rotor for 15 ml conical tubes, 45 Swing bucket rotor for 15 and 50 ml conical tubes, 40-place Horizontal rotor for 1.5-2.0 ml tubes.